Since when the coronavirus outbreak started in India, people came across these two words of science DNA and RNA. In a simple way, both DNA and RNA are related to genes in human beings. So, let us understand in-depth about them.
Nucleic acid: Nucleic acids which are macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides. There are two types of nucleic acids,
- DNA (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID)
- RNA (RIBONUCLEIC ACID)
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid simply is known as DNA is a thread of nitrogenous bases (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine) repeated over and over and arranged in a random thread-like structure. In the DNA genetic code is contained, in simple terms, it has the hereditary information which is passed on from parents to children. DNA is the genetic material found in living organisms, these organisms range from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals.
HISTORY OF DNA:
In 1866, Gregor Mendel first theorized the existence of inherited entities (genes). Later in 1869, Friedrich Miescher identified an acidic substance in the cell’s nuclei, this acidic substance was named as nuclein (which is now known as DNA). Although its existence was identified but was not studied in depth until in 1962, Watson, Crick, and Wilkins who described it and won a Nobel Peace Prize. The double-helical structure was proved by Rosalind Franklin even before the above-mentioned Nobel Laureates studied the structure of DNA thoroughly.

STRUCTURE OF DNA:
The name itself says that DNA is a nucleic acid, nucleic acids are the building blocks of all living organisms. Nucleotides are threaded next to each other through a phosphate backbone and are held together with their pairs through hydrogen bonds.
Differences and Similarities between DNA and RNA:
- Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids made up of nucleotides which are supported by a phosphate backbone. RNA is made using a model of existing DNA so that the genetic information is copied.
- DNA and RNA are responsible for the maintenance, imitation, and expression of hereditary information. DNA has the key to access hereditary information while RNA helps the DNA to unlock this information and shows what the obtained information is capable of. Together these two molecules make sure that the DNA is replicated (copied), the obtained information is translated, expressed, and that things go where they should go.
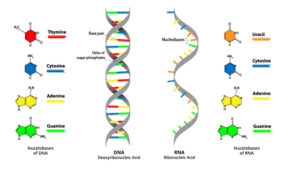
- One cannot talk about DNA without bringing up RNA, as they both work together. They are connected by the central dogma, which is the process of DNA transcription and translation for the purpose of protein synthesis which performs a number of tasks or functions in organisms.
- DNA and RNA, each have a negative backbone due to the phosphate group. They both have four nucleotides each, of the four nucleotides three of them are the same in both DNA and RNA (Guanine, Cytosine, and Adenine), the only difference being DNA has Thymine while RNA has Uracil. DNA is double-stranded, and RNA is single-stranded (threaded).
- DNA is found in the nucleus whereas RNA exists in the nucleus and as well as the cytoplasm. DNA is long-lived, and RNA is regenerated with each reaction. However, they are both central to cell function.