EHS Officer—The Safety Guardian
Table of Contents
The Person Who Prevents Disasters: EHS Officer
Manufacturing involves hazards: heavy machinery, chemicals, high temperatures, electrical systems, noise. One safety failure can cause serious injury or death.
EHS Officers (Environment, Health & Safety) are responsible for preventing these disasters. They earn ₹30,000-48,000/month as entry-level coordinators, advancing to ₹60,000-1,00,000+/month within 6-8 years as managers or directors.
What EHS Officers Actually Do:
Sneha, EHS Officer at a chemical manufacturing facility:
Monday: Incident Investigation
Worker got minor chemical burn—not serious, but any incident gets investigated.
Sneha:
- Interviews worker: What happened?
- Reviews work procedure: Did worker follow correct steps?
- Inspects site: Were safety guards in place?
- Checks PPE: Was protective equipment available and used?
- Finds: Worker wasn’t wearing gloves (didn’t realize they were needed)
- Root cause: Procedure wasn’t clear; previous worker did same thing without incident (luck)
- Action: Updates procedure with clearer guidance, adds warning sign, conducts training
Wednesday: Safety Audit
Quarterly internal audit of all safety procedures:
- Walks entire facility systematically
- Checks fire extinguishers (properly located, charged, current inspection tags?)
- Verifies emergency exits (unlocked, clearly marked, unobstructed?)
- Checks PPE availability (helmets, gloves, eye protection accessible where needed?)
- Inspects safety equipment (guardrails secure, warning signs visible?)
- Interviews workers: “Do you feel safe? Any concerns?”
- Documents findings: 3 minor issues (PPE not restocked after recent use, one guardrail loose, emergency contact info outdated)
- Issues corrective action report: All issues fixed within 2 days
Thursday: Regulatory Compliance Review
Manufacturing must comply with OSHA standards, environmental regulations, state safety laws. Sneha:
- Reviews latest regulatory updates (do regulations change?)
- Audits compliance: Are we following regulations?
- Finds: New regulation requires monthly inspection of pressure vessels
- Implements: Adds monthly inspection schedule, trains personnel
- Documents: Maintains compliance records
Friday: Near-Miss Program Review
Company has a “near-miss” program: Workers report incidents that almost happened but didn’t.
Sneha reviews this week’s near-misses:
- “Material almost fell from shelf onto worker” (shelf was overloaded)
- “Worker almost slipped on wet floor” (spilled liquid not cleaned promptly)
- “Equipment almost ran without safety guard” (worker forgot to engage guard)
For each:
- Investigates root cause
- Implements corrective action (reduce shelf load, mop spills immediately, enforce guard verification)
- Communicates lessons to all workers
- Tracks trends (if patterns emerge, addresses systematically)
Ongoing: Safety Culture Development
- Conducts monthly safety training (new procedures, refreshers, hazard awareness)
- Maintains safety bulletin board (regulations, incident reports, safety tips)
- Organizes safety committee meetings (workers + management discussing safety)
- Recognizes safety achievements (workers without incidents praised publicly)
- Communicates with management on safety metrics
Result: Facility has gone 2 years without serious incident. Workers feel safe. Regulatory compliance verified. Insurance premiums lower.
Key Responsibilities of EHS Officer
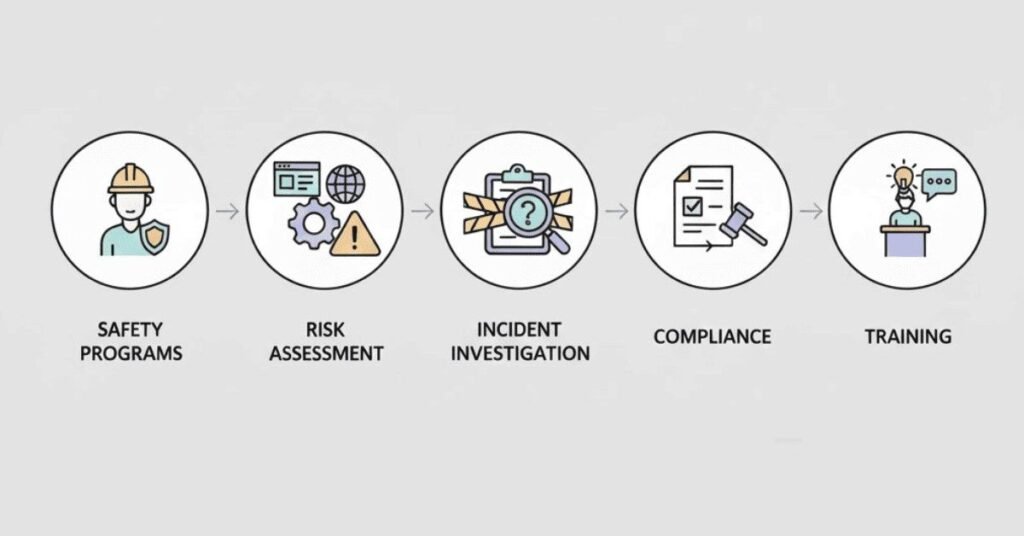
Safety Program Management (30%):
- Develop safety policies and procedures
- Implement safety programs
- Maintain safety equipment
- Coordinate safety training
- Manage incident prevention
Risk Assessment & Management (25%):
- Identify workplace hazards
- Assess risk levels
- Implement hazard controls
- Monitor effectiveness of controls
- Update as conditions change
Incident Investigation (20%):
- Investigate accidents and near-misses
- Identify root causes
- Implement corrective actions
- Prevent recurrence
- Document all findings
Regulatory Compliance (15%):
- Maintain compliance with OSHA standards
- Follow environmental regulations
- Keep required documentation
- Prepare for regulatory audits
- Stay current on changing regulations
Training & Communication (10%):
- Conduct safety training
- Communicate hazards and procedures
- Educate workers on safety importance
- Create safety culture
Build worker engagement
Technical Skills You Need
Core EHS Skills:
- Safety Standards Knowledge (Critical)
- OSHA standards (U.S. standards applicable to global companies)
- Industry-specific standards (varies by sector: pharma, automotive, chemicals)
- Environmental regulations
- Health standards (ergonomics, noise exposure, chemical safety)
- Why: Your job is ensuring compliance
- Learning: OSHA training courses (40-60 hours)
- Risk Assessment Methodologies (Important)
- Hazard identification techniques
- Risk assessment matrices
- FMEA (Failure Mode & Effects Analysis) applied to safety
- Severity-probability assessment
- Why: Systematically identify and reduce risks
- Learning: Training courses (30-40 hours)
- Incident Investigation (Important)
- Root cause analysis techniques (5-why method, fishbone diagrams)
- Investigation procedures
- Documentation
- Corrective action planning
- Why: Learn from incidents, prevent recurrence
- Learning: Training courses (20-30 hours)
- Environmental Knowledge (Increasingly Important)
- Environmental regulations (waste disposal, emissions, water discharge)
- Sustainability principles
- Environmental impact assessment
- Why: “E” in EHS increasingly important as sustainability emphasized
- Learning: Environmental management courses (30-50 hours)
- Workplace Health & Ergonomics (Important)
- Occupational health standards
- Ergonomic assessments
- Noise, lighting, ventilation requirements
- Chemical hazard communication
- Why: Worker health is critical EHS responsibility
- Learning: Occupational health courses (30-40 hours)
Additional Technical Skills:
- Legal knowledge (understanding safety laws)
- Statistics (analyzing incident data, trends)
- System design (designing safety into processes)
Psychology (building safety culture, behavior change)
Soft Skills for Success
Communication:
- Explain safety concepts to workers at all levels
- Present data and recommendations to management
- Train large groups effectively
- Communicate safety policies clearly
- Listen to worker concerns
Leadership:
- Build safety culture where workers care about safety
- Influence without authority (safety team members may not report to you)
- Coach and mentor safety coordinators
- Lead by example (follow safety procedures yourself)
Problem-Solving:
- Investigate complex incidents
- Find root causes systematically
- Develop practical solutions
- Think about system improvements
Credibility & Integrity:
- Maintain consistent standards for all
- Follow up on every incident
- Demonstrate genuine commitment to safety
Build trust with workers and management
Salary Expectations for EHS Officer
EHS Coordinator / Junior EHS Specialist:
₹26,000 – ₹40,000/month
(Entry-level, support role)
EHS Officer / Health & Safety Officer:
₹40,000 – ₹60,000/month
(Primary responsibility for facility)
Senior EHS Officer / Safety Manager:
₹60,000 – ₹90,000/month
(Multiple facilities or large facility oversight)
EHS Manager / Director:
₹90,000 – ₹1,40,000/month
(Department leadership, strategy)
Why Salaries Grow in EHS:
- Liability: Safety failures cost companies enormously (lawsuits, fines, reputation)
- Regulatory: Increasing regulations make EHS role more critical
- Insurance: Good safety record reduces insurance premiums (company saves money)
- Specialization: EHS experts with deep industry knowledge command premium
International: Global companies need EHS directors who understand multiple regulatory regimes
How to Enter EHS
Path 1: Manufacturing Role + EHS Transition
- Start in manufacturing (any role: production, maintenance, engineering)
- Show interest in safety: Volunteer for safety committee, suggest improvements
- Complete OSHA training (40-hour course: ₹15,000-25,000)
- Pursue EHS certification (see below)
- Transition to EHS coordinator (₹30,000-42,000/month)
Path 2: Engineering/Science Background + EHS Training
- Have degree in engineering, environmental science, or related field
- Pursue EHS certifications (OSHA, IOSH, etc.)
- Enter EHS specialist role directly (₹35,000-48,000/month)
Path 3: EHS Specialized Degree
- Complete EHS degree or diploma (specialized programs available)
Enter EHS coordinator role (₹30,000-42,000/month)
Certifications That Boost EHS Career
Entry-Level Certifications:
- OSHA 30-Hour Course: Foundational, highly recommended
- Cost: ₹10,000-18,000, Duration: 30 hours (online/classroom)
- ROI: Essential for any EHS role
Professional Certifications:
- IOSH (Institution of Occupational Safety & Health) Managing Safely: +₹5,000-8,000/month
- Cost: ₹40,000-60,000, Duration: 3 days + self-study
- ROI: Internationally recognized, highly valued
- Certified Safety Professional (CSP): Advanced certification, +₹12,000-20,000/month
- Requires experience + exam
- Cost: ₹50,000-1,00,000
- ROI: Top-tier EHS credential; path to senior roles
Specialization Certifications:
- Certified Environmental Compliance Auditor (CECA): +₹8,000-12,000/month
- Risk Assessment Certification: +₹5,000-8,000/month
Career Progression: Coordinator to Director
Year 1: EHS Coordinator
- Support EHS programs, coordinate training
- Salary: ₹28,000-40,000/month
Year 2-3: EHS Officer
- Primary responsibility for facility safety
- Lead incident investigations
- Salary: ₹40,000-60,000/month
Year 4-5: Senior Officer / EHS Manager
- Oversee multiple facilities or large facility
- Develop safety strategy
- Team leadership
- Salary: ₹60,000-90,000/month
Year 6+: EHS Director
- Executive role, board-level responsibility
- Company-wide safety strategy
Salary: ₹90,000-1,40,000+/month
The Bottom Line: EHS is Non-Negotiable Career
Every facility needs EHS professionals. Companies are increasingly focused on safety and sustainability. Entry salary ₹28,000-42,000 → 5-year salary ₹60,000-90,000+. The work is meaningful (preventing injuries, protecting environment), strategically important, and growing.
If you care about worker safety and environmental protection, EHS is your fulfilling career path.
