Automation Technician—The Future is Now
The Person Who Programs Robots: Automation Technician
Table of Contents
Visit a modern automotive assembly facility. Robots are everywhere—assembling components, welding parts, moving materials, placing components with precision. Who keeps these robots working? Automation technicians.
These aren’t people who just watch robots. They:
- Install and program robots
- Troubleshoot when robots malfunction
- Optimize robot performance
- Integrate robots with other systems
- Train operators on robot operations
- Design robotic workflows
And they’re earning ₹35,000-55,000/month for entry-level roles, with advancement to ₹60,000-1,00,000+/month within 5-7 years.
Automation and robotics specialization is among the fastest-growing areas in manufacturing, with severe shortage of skilled automation technicians driving premium salaries.
What Automation Technicians Actually Do
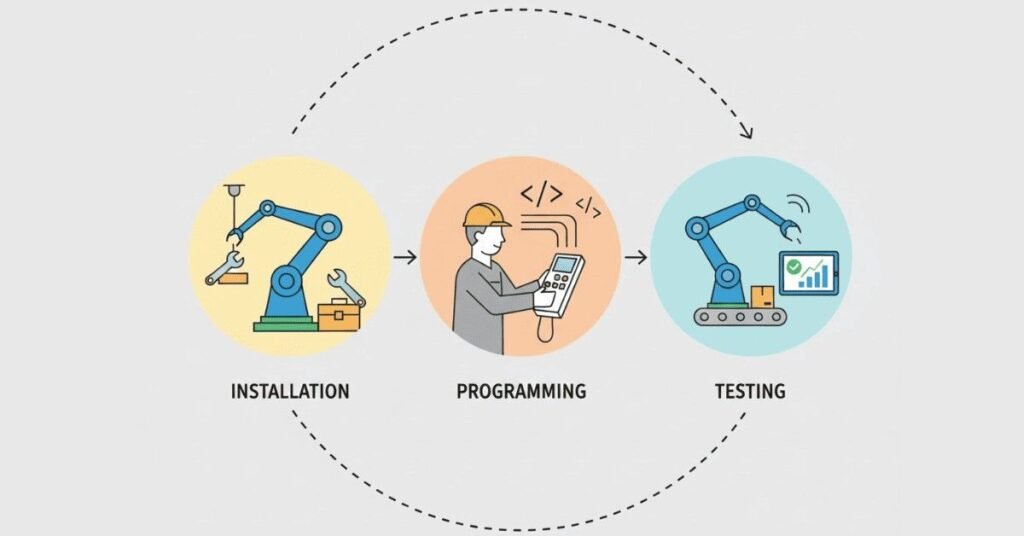
Priya, Automation Technician at an Electronics Assembly Facility
Challenge: Install New Robotic Arm for Component Placement
Company invested ₹50 lakhs in a new robot. Priya’s job: Install it and get it working.
Day 1-2: Installation
- Receives robot: Ensures all components arrived undamaged
- Studies documentation: Reviews installation manual, technical specifications, safety requirements
- Prepares site: Ensures proper floor space, power connections, air pressure connections
- Mounts robot: Securely fastens robot to foundation—precision matters (misalignment affects accuracy)
- Connects systems:
- Electrical: Connects to control power, ensures proper voltage
- Pneumatic/Hydraulic: Connects fluid lines with correct pressures
- Mechanical: Attaches end-effector (gripper, tool, etc.)
- Electrical: Connects to control power, ensures proper voltage
- Tests connections: Checks all systems operate correctly before programming
Day 3-5: Programming
- Learns programming language: Robot-specific (ABB, KUKA, Fanuc each have different languages)
- Creates program: Writes sequence of movements for robot to perform
- Pick component from tray
- Move to assembly position
- Place component
- Verify placement
- Return to home
- Repeat
- Pick component from tray
- Tests program:
- Dry run (moves without actually picking)
- Verification (movements happen in correct sequence)
- Troubleshooting (fixes any errors)
- Dry run (moves without actually picking)
- Optimizes:
- Reduces cycle time (faster movements, better sequencing)
- Improves accuracy (smoother paths, better positioning)
- Increases reliability (removes potential failure points)
- Reduces cycle time (faster movements, better sequencing)
Result: Robot now places 2,000 components daily with 99.8% accuracy (compared to humans: 85% accuracy, 500 components/day)
Day 6: Training & Integration
- Trains operators: Shows how to use robot, what buttons to press, safety procedures
- Integrates with production: Robot connects to conveyor system, quality inspection system, material supply
- Tests full workflow: Component arrives → Robot picks → Places → Moves to inspection → Quality system verifies
- Monitors: First 100 components manually reviewed to verify robot accuracy
- Documents: All programming code, safety procedures, maintenance requirements documented
Result: Robot successfully integrated into production. Increasing productivity by 40%.
What This Shows:
Priya’s role required:
- Technical knowledge (robotics, electrical, programming)
- Problem-solving (troubleshooting when issues arise)
- Hands-on skills (installation, wiring, mechanical setup)
- Software knowledge (robot programming languages)
- Learning ability (each robot type is different)
- Communication (training operators, explaining to supervisors)
This is modern technical work at a premium level.
Types of Automation Technician Specializations
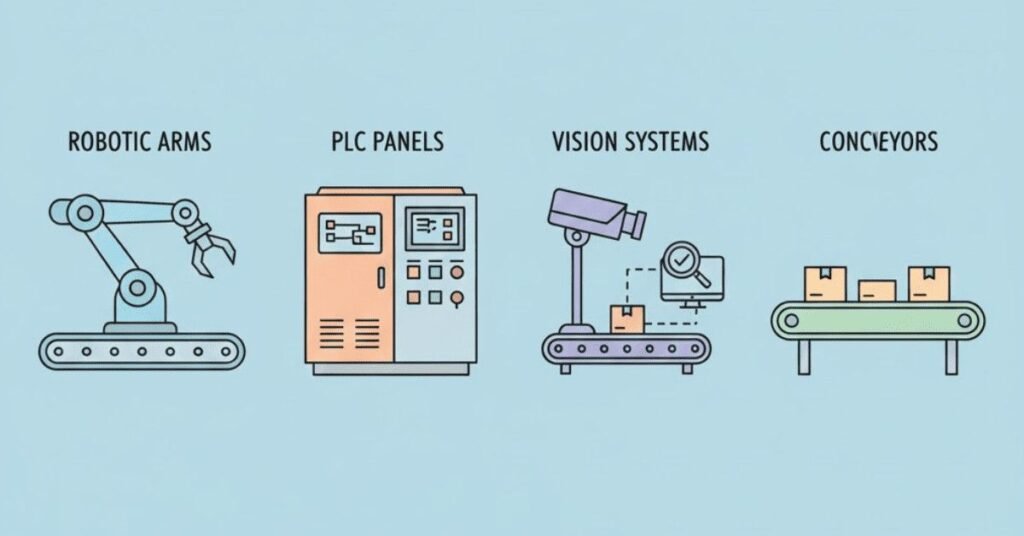
Specialization 1: Robotic Arm Technician
What They Do:
- Install robotic arms (6-axis, collaborative robots)
- Program arm movements and sequences
- Integrate with production systems
- Troubleshoot arm failures
- Optimize performance
- Train operators
Skills Required:
- Robotics programming (teach pendant operation)
- Understanding of robotic kinematics (how robots move)
- Electrical and mechanical troubleshooting
- End-effector (gripper) programming and adjustment
- Safety standards for collaborative robots
Entry Path:
- Mechanical/Electrical ITI + Robotics certification (3-6 months)
- Starting salary: ₹28,000-38,000/month
After 3 years: ₹48,000-65,000/month
Specialization 2: PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Technician
What They Do:
- Program PLCs that control manufacturing equipment
- Design control logic for production sequences
- Troubleshoot control system failures
- Integrate PLCs with sensors and motors
- Commission new production lines
- Train operators on control systems
Skills Required:
- PLC programming languages (ladder logic, structured text)
- Industrial electrical knowledge
- Sensor and motor interfacing
- HMI (Human Machine Interface) programming
- Troubleshooting logic errors
- Safety systems knowledge
Entry Path:
- Electrical ITI + PLC certification (4-6 months)
- Starting salary: ₹26,000-36,000/month
After 3 years: ₹45,000-60,000/month
Specialization 3: Vision System Technician
What They Do:
- Install and program automated vision systems
- Configure cameras for quality inspection
- Program defect detection algorithms
- Troubleshoot vision system errors
- Integrate vision with production control
- Maintain camera systems
Skills Required:
- Camera and lens knowledge
- Image processing basics
- Vision software programming (specific to vision systems)
- Lighting design for vision systems
- Integration with control systems
- Quality standards knowledge
Entry Path:
- Electronics/IT background + Vision system certification (3-4 months)
- Starting salary: ₹30,000-40,000/month
- After 3 years: ₹50,000-70,000/month
Specialization 4: Conveyor & Material Handling Systems
What They Do:
- Install conveyor systems
- Program conveyor control logic
- Integrate with sorting/diverting equipment
- Troubleshoot conveyor failures
- Optimize throughput
- Train operators
Skills Required:
- Conveyor system mechanics
- Motor and drive control
- Logic programming
- Sensor integration
- Belt alignment and maintenance
- Troubleshooting mechanical and electrical issues
Entry Path:
- Mechanical ITI + Conveyor system training (2-3 months)
- Starting salary: ₹24,000-32,000/month
After 3 years: ₹42,000-55,000/month
Key Responsibilities of Automation Technician
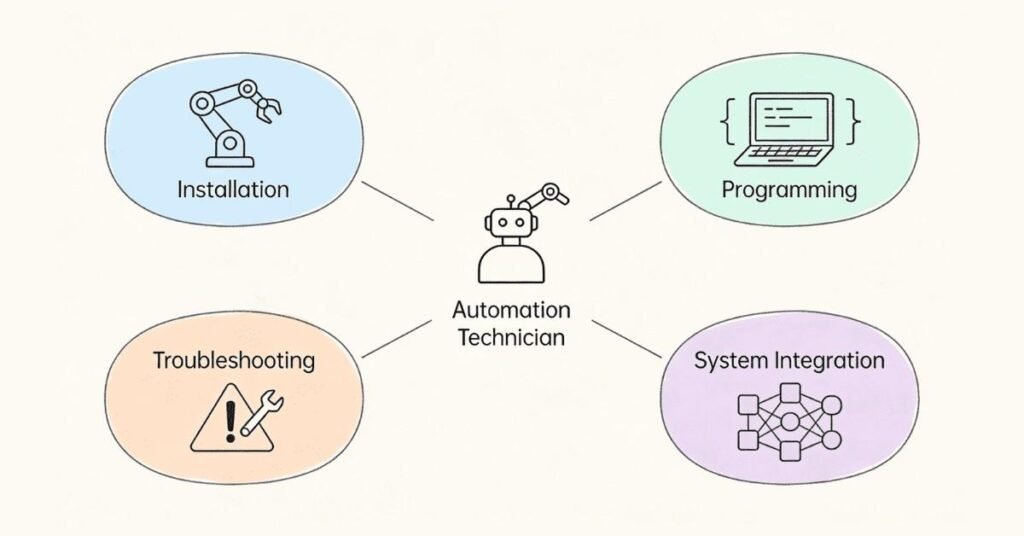
Installation & Setup (25% of role):
- Install automation equipment per specifications
- Connect electrical, pneumatic, hydraulic systems
- Mount and align equipment precisely
- Test all connections
- Perform safety checks
Programming & Configuration (30% of role):
- Write control logic and programs
- Configure sensors and actuators
- Program robot movements
- Create automation sequences
- Troubleshoot programming errors
- Optimize performance
Troubleshooting & Maintenance (25% of role):
- Diagnose automation system failures
- Repair or replace failed components
- Perform preventive maintenance
- Monitor system health
- Document issues and solutions
Integration & Testing (15% of role):
- Integrate automation with production systems
- Test full system workflow
- Verify quality and safety
- Commission new systems
- Train operators
Continuous Improvement (5% of role):
- Optimize cycle times
- Improve accuracy
- Reduce failures
- Suggest improvements
Skills You Need
Technical Skills (Critical):
- Understanding of automation and robotics
- Electrical troubleshooting and connections
- PLC or robot programming (language-specific)
- Sensor and actuator knowledge
- Systems integration
- Safety standards (ISO 10218 for robots, machine safety)
- CAD basics for system design
Practical Skills:
- Tool proficiency (wiring, mechanical assembly)
- Electrical measurement and testing
- Precision installation
- Mechanical alignment
- Problem-solving under pressure
Software Skills:
- Robot programming languages (ABB RAPID, KUKA KRL, Fanuc TPP)
- PLC programming (ladder logic, structured text)
- HMI software
- Computer skills and software troubleshooting
Soft Skills:
- Communication (explaining systems to operators)
- Documentation (detailed procedures)
- Learning ability (new equipment constantly emerging)
- Attention to detail (misalignment causes problems)
Safety consciousness
Salary Expectations for Automation Technician
Entry-Level Automation Technician:
₹26,000 – ₹38,000/month
(Higher than mechanical fitter due to specialization)
With Shift & Performance Bonuses:
- Base: ₹32,000
- Shift allowance: +₹2,000-3,000
- Performance bonus: +₹2,000-4,000
- Actual take-home: ₹36,000-42,000/month
After 2-3 Years (Senior Automation Technician):
₹42,000 – ₹58,000/month
After 5 Years (Lead / Team Lead):
₹58,000 – ₹80,000/month
Career Advancement to Engineering:
With additional education (diploma or degree in automation/control engineering):
- Transition to Automation Engineer
- Salary: ₹60,000-95,000/month
- Responsibility increases significantly
Why Automation Salaries Are Premium:
- Specialized expertise: Fewer people have skills
- High business impact: Automation directly improves productivity (measurable ROI)
- Strategic importance: Automation is central to Industry 4.0 vision
- Growing demand: Every factory is automating; shortage of skilled technicians
Future-proof: Automation only increasing, not decreasing
How to Become an Automation Technician
Recommended Path:
- Complete ITI (Electrical or Mechanical): 2-3 years
- Foundational knowledge in electrical systems or mechanics
- Cost: ₹20,000-40,000
- Benefit: Immediate job eligibility for technician roles
- Foundational knowledge in electrical systems or mechanics
- Pursue Robotics/PLC Certification: 3-6 months
- Specialized training in robotics or PLC programming
- Cost: ₹30,000-60,000
- Providers: FANUC, ABB, Siemens, Bosch (brand-specific training)
- Benefit: Certification from equipment manufacturers increases credibility
- Specialized training in robotics or PLC programming
- First Job: Automation Technician (₹26,000-38,000/month)
- Work for 2-3 years gaining experience
- Master specific automation systems (robots, PLCs, vision)
- Build portfolio of successful projects
- Work for 2-3 years gaining experience
- Advancement: Senior Technician → Lead Technician → Automation Engineer (with additional education)
Alternate Path (If You Have Engineering Background):
- Complete automation-specific engineering course/diploma
- Graduate Engineer Trainee in automation or controls
- Direct entry into junior automation engineer roles
- Faster advancement to engineer/manager roles
Certifications That Boost Automation Technician Career
Robot Manufacturer Certifications (Most Valuable):
- FANUC Certified Technician
- ABB Certified Technician
- KUKA Certified Technician
- Siemens Certified Technician
- Benefit: ₹8,000-15,000/month salary boost
- Cost: ₹40,000-80,000
- Duration: 2-4 weeks intensive
- ROI: Very high (certification directly translates to jobs and salary)
PLC Certifications:
- Siemens S7 Certified
- Allen-Bradley Certified
- Benefit: ₹6,000-12,000/month salary boost
- Cost: ₹25,000-50,000
- Duration: 4-8 weeks
Six Sigma Green Belt:
- Can complement automation expertise
- Benefit: ₹5,000-8,000/month additional
Cost: ₹20,000-35,000
Why Automation Technician is Your Best Choice If You Like Technology
Advantages:
- Cutting-edge technology: Working with robots, AI, Industry 4.0
- High salary potential: Specialization commands premium, fastest growing sector
- Recession-proof: Automation adoption accelerating regardless of economy
- Global opportunities: Every country needs automation technicians; international assignments likely
- Engaging work: Problem-solving with advanced systems
- Career advancement: Clear path to automation engineer, manager, or specialization
- Future-proof: This is the future of manufacturing
When It Might Not Be Ideal:
- If you dislike learning new technologies constantly
- If you’re uncomfortable with electrical systems
- If you prefer hands-on mechanical work over electronic systems
- If you dislike continuous travel (some roles require travel for installations)
The Bottom Line: Automation Technician is the Future Technical Career
While mechanical fitters work with established technology, automation technicians work at the frontier of manufacturing innovation. Salaries are premium, job security is excellent, and the career trajectory is clear: technician → senior technician → technician lead → automation engineer.
Starting salary ₹28,000-38,000/month → 5-year salary ₹58,000-80,000+/month. The work is genuinely interesting. The future is automation; automation technicians build that future.
