Let us Discuss About who is Data Analyst?
A data analyst serves as a gatekeeper for the data of an organization, enabling stakeholders to understand the information and make strategic business decisions. It is a technical role that requires a bachelor’s degree or master’s degree in analytics, computer modeling, science, or mathematics.
What is Analytics?
Analytics brings together both conceptual frameworks and real world uses to identify and communicate insights based on data. This process helps mangers, shareholders, and other executives within an organization make better informed decisions. Experience also shows that skilled analysts view their work as being set in a much larger context, where both internal dynamics and numerous external factors come into play. They are able to take into account the competitive landscape, the interests of both internal and external business entities, and the limitations posed by missing datasets when formulating data driven recommendations for stakeholders.
The role and responsibilities of a data analyst are quite wide ranging and essential for organizations that rely on data driven decision making. The key responsibilities derived from the analyzed sources are as follows:
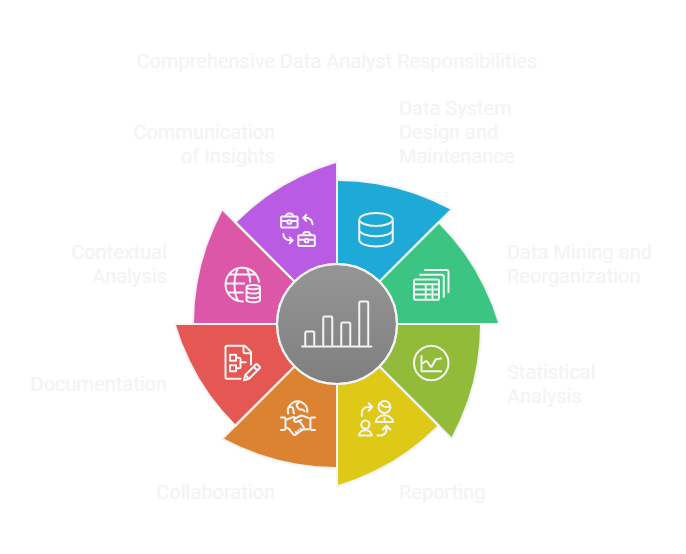
Key Responsibilities of a Data Analyst
1. Data System Design and Maintenance
- Design and maintain data systems and databases, ensuring they are functional and efficient.
- Fix coding errors and resolve other data related issues.
2. Data Mining and Reorganization
Extract data from both primary and secondary sources. Reorganize the data into formats that are easily interpretable by humans or machines.
3. Statistical Analysis
Utilize statistical tools to analyze datasets, focusing on identifying trends and patterns that inform diagnostic and predictive analytics.
4. Reporting
Prepare comprehensive reports for executive leadership that communicate significant trends, patterns, and predictions based on analyzed data.
5. Collaboration
Work collaboratively with programmers, engineers, and organizational leaders to identify opportunities for process improvements.
Recommend system modifications and develop policies for effective data governance.
6. Documentation
Create documentation that outlines the steps taken during the data analysis process, allowing stakeholders to replicate analyses if necessary.
7. Contextual Analysis
Demonstrate the relevance of findings in relation to local, national, and global trends impacting the organization and its industry.
8. Communication of Insights
Communicate insights driven from data analyses to stakeholders helps organizations make informed, strategic business decisions.
These involve the key characteristics of a professional data analyst for the transformation of raw data to actionable insights used in strategic planning and decision support within organizations.
What Skills Do You Need to be a Data Analyst?
A successful data analyst will have a mix of technical skills and leadership skills.
Technical skills are the knowledge of database languages, such as SQL, R, or Python; spreadsheet tools for statistical analysis, such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets; and data visualization software, such as Tableau or Qlik. Mathematical and statistical skills are also useful in gathering, measuring, organizing, and analyzing data with these common tools.
Common Challenges Data Analysts Face in Their Roles
-
Constraints and Data Volumes
The major challenge that most data analysts face is the issue of time. Data analysis can be very time-consuming, especially when dealing with large quantities of data. Moreover, results are only as accurate and valid as the data utilized. There is, thus, a need to know all the information pertinent to analysis to streamline activities in data analysts’ roles and responsibilities.
2. Managing Expectations
Data analysts will have to learn to manage the stakeholders’ expectations for what can be done with available data. For instance, difficult conversations may ensue around limitations of available data sets or having to prioritize work to ensure the most important initiatives get completed first.
3. Data Quality
Low-quality data can result in unreliable outcomes and erroneous conclusions. Consequently, it is crucial for data analysts to thoroughly comprehend the data they handle and recognize any possible problems or deficiencies. This necessitates performing data cleaning and validation to guarantee accuracy and dependability.
4. Keeping up with Technology
Indeed, the world of big data grows fast, and it means one has to be alert about new trends and technological inventions. Information about cloud computing, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and the rest is very essential in keeping one at the top and delivering something impactful from data.
To read more blogs CLICK HERE
