Pharmacist Career – Opportunities Beyond the Pharmacy Counter
Table of Contents
Introduction: Pharmacy is Much Bigger Than You Think
Picture this: You’re sitting in a hospital pharmacy watching a clinical pharmacist. She’s not just counting pills. She’s reviewing a patient’s medications, noticing a dangerous drug interaction that the doctor missed. She alerts the doctor, who changes the prescription. The patient’s life is literally saved by that pharmacist’s expertise.
That’s modern pharmacy. That’s why pharmacists are increasingly valuable in healthcare organizations.
Here’s what most people don’t know about pharmacy: It’s not just about retail pharmacy counters. When people think “pharmacist,” they imagine someone behind a glass counter dispensing medications to customers. That role still exists, but it’s just one tiny corner of an enormous profession.
Modern pharmacists work as:
- Clinical pharmacists in hospitals making life-or-death medication decisions
- Pharmaceutical researchers developing new drugs
- Pharmacovigilance specialists ensuring drug safety globally
- Healthcare consultants optimizing medication use
- Pharmaceutical sales experts connecting treatments to patients
- Regulatory affairs specialists navigating FDA approvals
- Medical writers communicating complex science
- Hospital administrators managing pharmacy operations
- Entrepreneurs starting healthcare businesses
The beautiful part? Pharmacy offers exceptional job security, decent salary progression (₹2.5 LPA starting to ₹15-20 LPA for experienced professionals), and genuine career flexibility.
If you’re considering B.Pharm, this guide reveals opportunities you probably don’t know existed.
What is B.Pharm? The 4-Year Degree That Opens Multiple Doors
B.Pharm (Bachelor of Pharmacy) is a 4-year undergraduate degree that trains you in pharmaceutical science, drug interactions, patient care, and healthcare systems. But describing it this way is boring. Let’s explain what you actually learn.
What You’ll Study in B.Pharm
Year 1-2: Foundation (Semesters 1-4)
You’ll learn the basics of pharmacy science:
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry: How drugs are made, chemical structures, synthesis
- Pharmacology: How drugs work in the body, side effects, mechanisms
- Pharmaceutics: Drug formulation, manufacturing, delivery systems
- Anatomy & Physiology: How the body works (essential for understanding disease)
- Biochemistry: Chemical processes in living cells
- Pathology: How diseases damage the body
- General Science: Mathematics, physics, statistics relevant to pharmacy
This foundation is crucial. You need to understand WHY a drug works, not just THAT it works.
Year 3: Practical Application (Semesters 5-6)
Theory meets practice:
- Clinical Pharmacy: Using drugs to treat patient diseases
- Pharmacy Practice: Hospital operations, ethical practice, legal requirements
- Medicinal Chemistry: Drug design and development
- Pharmaceutical Analysis: Testing drug purity and effectiveness
- Pharmaceut Management: Business aspects of pharmacy
- Hospital Pharmacy Practice: Real-world hospital operations
Year 4: Specialization & Internship (Semesters 7-8)
- Advanced Clinical Pharmacy: Complex patient cases, drug interactions
- Pharmacovigilance: Drug safety, adverse effects reporting
- Research Project: Conducting original pharmacy research
- 6-Month Hospital Internship: Real clinical experience dispensing, consulting, counseling
By the end, you’re not just pharmacy graduate—you’re clinically trained and ready for specialized roles.
B.Pharm Eligibility & Admission
Who Can Pursue B.Pharm:
- 12th pass with Physics, Chemistry, Biology (PCB)
- Minimum 50% marks in 12th typically
- Age: Usually 17-35 years
- Through entrance exams (state and national level) or merit-based admission
Entrance Exams:
- NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test): Used for government medical and pharmacy colleges in most states
- State-level exams: Some states conduct their own pharmacy entrance exams
- Merit-based: Some private colleges admit based on 12th marks
- Direct admission: Some colleges admit directly (though quality varies)
Government vs Private B.Pharm Colleges:
- Government colleges: Better quality, lower fees (₹1-3 lakhs total), competitive admission, better placements
- Private colleges: Higher fees (₹5-15 lakhs total), easier admission, variable quality
Recommendation: Aim for government pharmacy colleges if possible. Quality is better, and you save significant money.

Different Types of Pharmacist Roles: Your Options
Here’s where pharmacy becomes interesting. After B.Pharm, you have multiple career paths. Let’s explore each honestly.
Role 1: Retail Pharmacist – The Traditional Path
What They Do:
- Dispense medications to customers
- Answer medication questions
- Counsel patients on proper use
- Manage pharmacy inventory
- Handle insurance and billing
- Manage pharmacy staff (if store manager)
Work Environment:
- Pharmacy shops, medical stores, retail chains
- Typical 8-10 hour shifts
- High customer interaction
- Fast-paced environment
- Often standing all day
Salary:
- Entry-level: ₹2.5-3.5 LPA
- Experienced (5+ years): ₹4-6 LPA
- Store manager/owner: ₹6-15 LPA depending on success
Advantages:
- Clear, stable employment
- High customer interaction (if you enjoy this)
- Can eventually own your own pharmacy
- Decent earning potential with ownership
Disadvantages:
- Limited career advancement if staying in retail
- Repetitive work initially
- Physical demands (standing long hours)
- Limited learning and growth opportunities compared to clinical roles
- Not using full pharmaceutical knowledge
Real Talk: Retail pharmacy is the most common role for B.Pharm graduates initially. Nothing wrong with this, but be aware it’s not the only option. Many pharmacists start retail, gain experience, then transition to clinical roles.
Best For: Those preferring stable employment, retail business interests, entrepreneurial aspirations
Role 2: Hospital Pharmacist – The Evolving Clinical Role
What They Do:
- Manage hospital pharmacy operations
- Dispense medications for inpatients
- Prepare IV medications and compounds
- Consult with doctors on medication selections
- Monitor patient drug interactions
- Ensure drug safety and compliance
- Educate patients on medications
- Participate in clinical rounds
Work Environment:
- Hospital pharmacy departments
- Shift work (including nights, weekends)
- Collaboration with doctors, nurses, other clinicians
- High-pressure environment (medication errors have serious consequences)
- Mix of administrative and clinical work
Salary:
- Entry-level: ₹3-4.5 LPA
- Experienced (5+ years): ₹6-9 LPA
- Senior positions: ₹10-15 LPA
- Head of Pharmacy Department: ₹15-20+ LPA
Advantages:
- More clinically engaged work
- Making real patient impact decisions
- Better career advancement opportunities
- Specialization possibilities
- More intellectually stimulating than retail
- Clear ladder to senior positions
Disadvantages:
- Shift work and on-call requirements
- High responsibility and stress
- Requires strong clinical knowledge
- Potential conflicts with doctors
- Initial preparation demands
Real Opportunity: Hospital pharmacy is growing rapidly in India. As healthcare improves, hospitals increasingly employ pharmacists. This is where your clinical training gets used.
Best For: Those interested in clinical medicine, patient interaction, career advancement, stable employment
Role 3: Clinical Pharmacist – The Specialist
What They Do:
- Provide direct patient care
- Manage medication therapy
- Conduct patient consultations
- Specialize in specific areas (cardiology, oncology, diabetes, etc.)
- Conduct clinical research
- Educate healthcare teams
- Work in specialized clinics or units
Work Environment:
- Specialized hospital units or clinics
- More flexible hours than general pharmacy
- Direct patient interaction
- Autonomy in clinical decisions
- Collaborative with medical team
Education Required:
- B.Pharm + 1-2 years experience
- M.Pharm (Master’s degree) in clinical pharmacy
- Clinical pharmacist certification
Salary:
- Entry-level clinical pharmacist: ₹5-7 LPA
- Experienced: ₹8-12 LPA
- Specialist positions: ₹12-18 LPA
Advantages:
- Highest job satisfaction among pharmacy roles
- Direct patient impact
- Best salary among pharmacy roles
- International opportunities
- Leadership potential
- Continuous learning
Disadvantages:
- Requires additional education (M.Pharm)
- More responsibility and stress
- Limited positions available compared to retail/general hospital
- Requires strong communication skills
- Research component often required
The Real Picture: Clinical pharmacy is where pharmacy is evolving. Hospitals increasingly hire clinical pharmacists because they genuinely improve patient outcomes. If you love pharmacy and want intellectual challenge, this is your path.
Best For: Ambitious pharmacists, patient-focused professionals, those pursuing master’s degrees, career-driven individuals
Role 4: Pharmacovigilance Specialist – Drug Safety Expert
What They Do:
- Monitor adverse drug reactions (ADRs)
- Report safety issues to regulatory authorities
- Analyze drug safety data
- Maintain pharmacovigilance databases
- Investigate medication problems
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Prepare safety reports for global regulatory bodies
Work Environment:
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- Hospitals with large clinical trial programs
- Insurance companies
- Government regulatory agencies
- 9-5 office environment
Typical Roles:
- Drug Safety Associate (DSA): Entry-level, collecting and processing adverse event reports
- Pharmacovigilance Scientist: Analyzing safety data, identifying trends
- Pharmacovigilance Manager: Leading safety teams, regulatory interactions
Salary:
- Entry-level (DSA): ₹3-5 LPA
- Pharmacovigilance Scientist: ₹5-8 LPA
- Manager: ₹10-15 LPA
Advantages:
- Office-based work (no patient contact if you prefer)
- Good salary progression
- International exposure (global drug safety)
- Genuine impact on public health
- Growing field with lots of opportunities
- Regular hours
Disadvantages:
- Less patient contact
- Data-heavy, sometimes repetitive work
- Regulatory complexity
- Accountability pressure
The Opportunity: Pharmacovigilance is absolutely booming in India. Pharmaceutical companies need professionals monitoring drug safety. This is where you can work internationally without leaving India.
Best For: Detail-oriented professionals, data analysts at heart, those preferring office work, internationally-minded
Role 5: Pharmaceutical Sales Representative – The Business Side
What They Do:
- Promote medications to doctors and hospitals
- Provide product information
- Manage sales territories
- Attend medical conferences
- Build relationships with healthcare providers
- Meet sales targets
Work Environment:
- Field-based, visiting hospitals and clinics
- Travel-heavy (40-50% travel typical)
- Commission-based compensation
- Competitive environment
- Performance-driven
Salary:
- Entry-level: ₹3-4.5 LPA base + commission
- With commissions: ₹6-10 LPA typical
- Experienced: ₹10-20+ LPA with high commission achievers
Advantages:
- High earning potential with commission
- Field independence
- Meeting medical professionals
- Travel opportunities
- Sales skills development
Disadvantages:
- Heavy travel requirements
- Pressure-heavy environment
- Commission-dependent income variability
- Less clinically focused
- Ethical questions about pharmaceutical marketing
Real Talk: Pharma sales is lucrative but demanding. If you enjoy sales and travel, it’s excellent. But if you want clinical pharmacy, this isn’t your path.
Best For: Extroverts, sales-oriented professionals, travel enthusiasts, high-income seekers
Role 6: Regulatory Affairs & Pharmaceutical Quality
What They Do:
- Manage drug approvals and regulatory compliance
- Ensure medications meet quality standards
- Conduct quality control testing
- Manage regulatory documentation
- Liaise with FDA, drug regulatory authorities
- Handle product recalls and safety issues
- Manage pharmaceutical processes
Work Environment:
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing plants or offices
- Quality control labs
- Regulatory compliance departments
- 9-5 office/lab environment
- Collaborative with other departments
Salary:
- Entry-level (QC): ₹3-4.5 LPA
- Regulatory Affairs professional: ₹5-9 LPA
- Senior positions: ₹10-15 LPA
Advantages:
- Critical role in drug development
- Good salary
- Regular hours
- Clear career path
- Stability
Disadvantages:
- Less patient contact
- Regulatory complexity
- Sometimes repetitive documentation
- Less dynamic than clinical or sales
Best For: Detail-oriented professionals, those interested in manufacturing, process-focused individuals
Role 7: Pharmaceutical Research & Development
What They Do:
- Develop new medications
- Conduct drug trials
- Analyze research data
- Publish scientific findings
- Contribute to pharmaceutical innovation
Work Environment:
- Research labs, pharmaceutical companies
- Universities with research programs
- Contract Research Organizations
- Flexible hours for research work
- Highly intellectual environment
Salary:
- Entry-level (Research Associate): ₹3.5-5 LPA
- Senior Scientist: ₹8-12 LPA
- Research Director: ₹15-25+ LPA
Advantages:
- Cutting-edge science
- Innovation at the core
- Academic recognition
- International collaboration
- Highest intellectual challenge
- Publishing and recognition
Disadvantages:
- Requires master’s degree (M.Pharm) or PhD
- Long path to senior positions
- Competitive funding and positions
- Results uncertainty in research
Best For: Science-focused pharmacists, academic interests, research-oriented minds, PhD aspirants
Role 8: Hospital Administration & Management
What They Do:
- Manage hospital pharmacy department
- Handle budget and operations
- Staff management and training
- Vendor relationships
- Pharmacy strategy and planning
Work Environment:
- Hospital administrative offices
- Some on-floor supervision
- Meetings and administrative work
- Decision-making authorit
- Increasing responsibility
Salary:
- Pharmacy Manager: ₹8-12 LPA
- Head of Pharmacy: ₹12-18 LPA
- Hospital Director-level: ₹15-25+ LPA
Best For: Leadership-oriented pharmacists, business-minded professionals, management aspirations
B.Pharm Education: What to Expect, Cost, and Value
Let’s talk about the actual B.Pharm degree—what it costs, how long it takes, and whether it’s worth it.
Program Structure
Duration: 4 years (8 semesters) + 6-month internship = 4.5 years total
Cost:
- Government colleges: ₹1-3 lakhs total for 4.5 years (very affordable)
- Private colleges: ₹8-15 lakhs total (significant investment)
- Top private institutions: ₹20-30 lakhs (premium pricing)
Return on Investment:
- Government college investment: ₹2 lakhs, starting salary ₹3 LPA, recovered in ~8 months
- Private college investment: ₹12 lakhs, starting salary ₹3 LPA, recovered in ~4 years
Honest Assessment: Even private college fees are manageable given pharmacist salaries. ROI is positive within 4-5 years.
Is B.Pharm Worth It?
Why pursue B.Pharm:
- Stable career with consistent demand
- Multiple job paths and flexibility
- Decent salary progression (₹2.5 LPA → ₹15-20 LPA over 10 years)
- Professional respect
- Genuine impact on healthcare
- Job security
- Clear career advancement
When to think twice:
- If you hate chemistry, don’t pursue pharmacy
- If you want to work abroad immediately (requires licensing exams)
- If you prefer non-healthcare careers
- If you’re seeking ultra-high income (management/finance might pay more initially)
Bottom line: B.Pharm is solid career choice if you’re genuinely interested in healthcare and medications.collegesearch+1
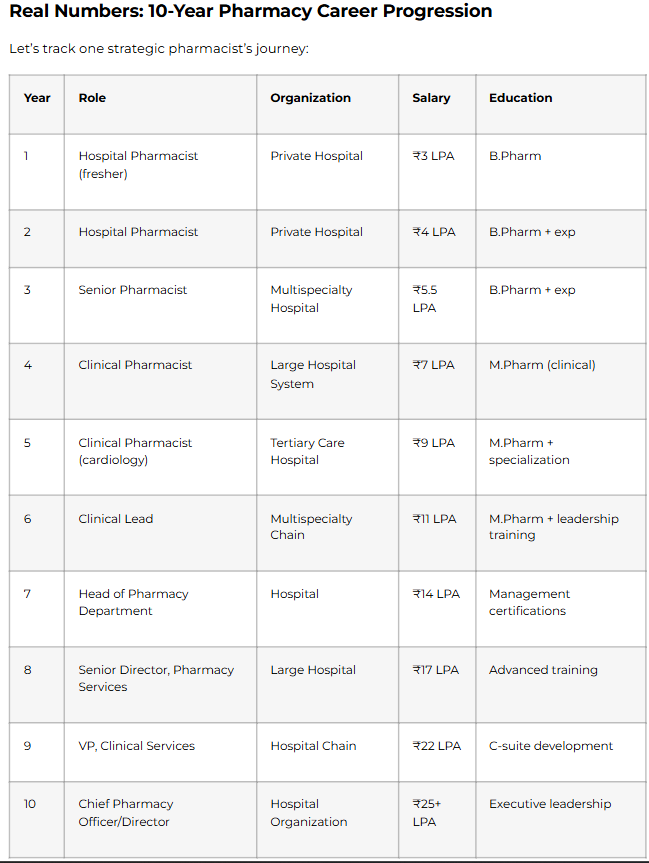
Salary Progression in Pharmacy: Realistic Numbers
Let’s talk actual numbers based on current market data.
Entry-Level (Fresh Graduate, 0-1 Year)
Typical Salary: ₹2.5-4 LPA
By Role:
- Retail pharmacist: ₹2.5-3.5 LPA
- Hospital pharmacist: ₹3-4 LPA
- Quality control: ₹3-4 LPA
- Sales representative: ₹3-5 LPA (with commission)
Location Matters:
- Metros (Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore): ₹3.5-4.5 LPA
- Tier-2 cities: ₹2.8-3.5 LPA
- Small cities/towns: ₹2.3-3 LPA
Why Lower Starting Salary:
Honestly? B.Pharm graduates aren’t highly specialized initially. You’re competing with many pharmacy graduates. Salary rises as you gain experience and specialize.
Getting Higher Starting Salary:
- Joining multinational pharmaceutical companies (₹4.5-6 LPA possible)
- Scoring high in entrance exams
- Internships at top hospitals (better placement offers)
- Additional certifications
- Pharmaceutical sales roles (commission potential)
Junior Professional (1-3 Years)
Typical Salary: ₹4-6 LPA
By Role:
- Hospital pharmacist (experienced): ₹4.5-6 LPA
- Pharmaceutical company: ₹4-7 LPA
- Retail manager: ₹5-7 LPA
- Clinical pharmacist (with M.Pharm): ₹5-7 LPA
- Pharmacovigilance scientist: ₹5-8 LPA
How to Jump to ₹6+ LPA:
- Get advanced certification (M.Pharm if possible)
- Specialize in high-demand area
- Move to hospital (better than retail initially)
- Switch to pharmaceutical company
- Show consistent excellence
Mid-Career (3-7 Years)
Typical Salary: ₹6-12 LPA
By Role:
- Hospital pharmacist (senior): ₹7-10 LPA
- Pharmaceutical sales (high performers): ₹8-15 LPA with commission
- Clinical pharmacist: ₹8-12 LPA
- Pharmacovigilance manager: ₹10-14 LPA
- Quality assurance lead: ₹8-12 LPA
- Retail owner (self-employed): ₹8-20+ LPA depending on success
Critical Earning Decisions at This Stage:
- Stay in current role vs. switch for growth
- Get master’s degree for advancement
- Move to specialized area
- Consider starting own pharmacy business
- Switch to pharmaceutical company
- Move to consulting or other roles
Senior Professional (7-12+ Years)
Typical Salary: ₹12-25+ LPA
By Role:
- Head of Hospital Pharmacy: ₹15-20 LPA
- Pharmaceutical company senior manager: ₹15-25 LPA
- Clinical pharmacist specialist: ₹12-18 LPA
- Pharmacovigilance director: ₹15-25 LPA
- Pharmaceutical business owner: ₹20-50+ LPA
Who Reaches Here:
- Top 10-15% of pharmacy graduates
- Consistent career progression
- Leadership skills
- Advanced education (master’s, sometimes PhD)
- Strategic career moves
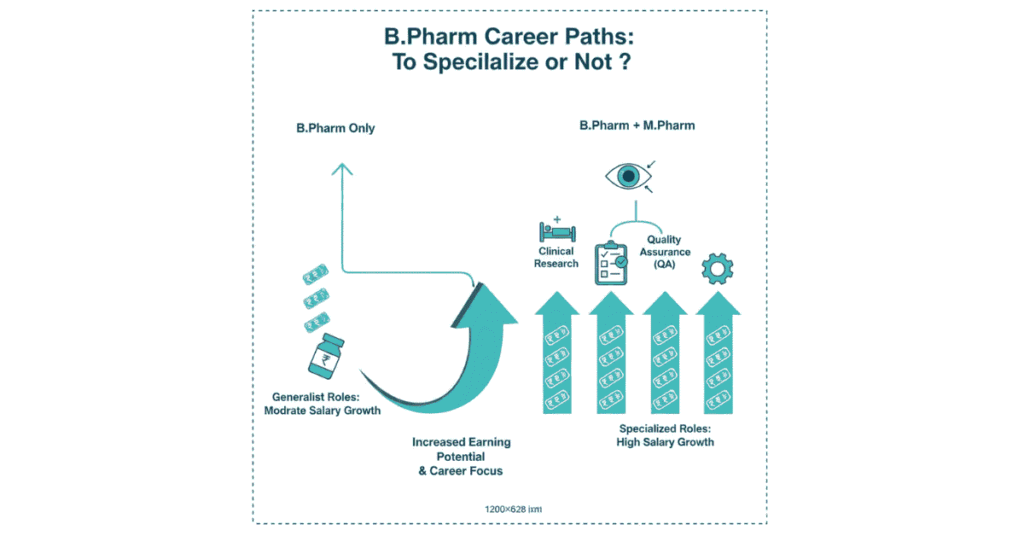
Master's Degree in Pharmacy (M.Pharm): Should You Pursue It?
One critical career decision: Do you pursue M.Pharm after B.Pharm?
What is M.Pharm?
Duration: 2 years (4 semesters)
Cost:
- Government colleges: ₹1-2 lakhs
- Private colleges: ₹5-10 lakhs
Specializations Available:
- Clinical Pharmacy: Patient-focused pharmaceutical care
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry: Drug design and development
- Pharmaceutics: Drug formulation and delivery
- Pharmacology: Drug mechanisms and effects
- Quality Assurance: Manufacturing quality
- Pharmaceutical Management: Business and administration
- Pharmacovigilance: Drug safety
Should You Do M.Pharm? Decision Framework
Do M.Pharm If:
- You’re aiming for clinical pharmacy roles
- You want to specialize in a high-demand area
- You’re interested in leadership positions
- You want to maximize salary potential
- You’re considering research or academia
- You can afford the additional education
Skip M.Pharm If:
- You want to start earning immediately
- You’re considering pharmacy retail business
- You’re not interested in specialization
- Financial constraints are significant
- You prefer getting experience before further study
M.Pharm ROI Calculation
Investment: ₹1-10 lakhs (depending on college)
B.Pharm salary without M.Pharm: ₹3 LPA
M.Pharm graduate salary: ₹5-7 LPA
Salary difference: ₹2-4 LPA annually
Payback period: 3-5 years typically
After that, M.Pharm holders typically earn significantly more. It’s a worthwhile investment for career growth
Essential Pharmacy Certifications & Specializations
Beyond the basic B.Pharm, certifications add serious value and salary potential.
Clinical Pharmacy Certifications
Certified Clinical Pharmacist (CCP):
- Duration: 6-12 months study
- Focus: Clinical pharmacy practice
- Salary boost: 20-30% increase
- Value: Opens clinical roles
Diabetes Education Certification:
- Focus: Diabetes patient management
- Salary boost: 15-25% increase
- Opportunity: Growing diabetes epidemic = high demand
Hypertension/Cardiovascular Specialization:
- Focus: Heart disease management
- Salary boost: 20-25% increase
- Opportunity: Cardiology is well-paying specialty
Pharmacovigilance Certifications
ICSR (Individual Case Safety Report) Training:
- Duration: 1-2 weeks
- Cost: ₹5,000-15,000
- Value: Required for pharmacovigilance roles
Advanced Pharmacovigilance Certifications:
- Duration: 3-6 months
- Cost: ₹20,000-50,000
- Salary boost: 30-50%
Management & Leadership Certifications
Pharmacy Management Certification:
- For those aiming for supervisor/manager roles
- Duration: 3-6 months
- Salary boost: 25-40%
MBA in Pharmaceutical Management:
- Duration: 2 years
- Cost: ₹6-15 lakhs
- Salary jump: Significant (₹8-12 LPA → ₹12-18 LPA)
Worth considering for leadership aspirations
Landing Your First Pharmacy Job: Strategy
Pharmacy Resume Template
text
[YOUR NAME]
City, State | Phone: +91-XXXXX-XXXXX | Email: yourname@email.com | LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/yourprofile
PROFESSIONAL SUMMARY
Healthcare-focused pharmacist with [X months/years] of pharmaceutical experience in [hospital/retail/industry] settings. Dedicated to patient medication education, clinical drug therapy optimization, and healthcare safety. B.Pharm graduate with strong pharmaceutical knowledge and excellent patient communication skills.
LICENSES & CERTIFICATIONS
- B.Pharm (Bachelor of Pharmacy) – [College Name] – [Year]
- Pharmacist License – [Registration Number] – [Issuing Authority]
- [Any specialty certifications – e.g., CCP, Diabetes Education]
PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE
Hospital Pharmacist Intern | [Hospital Name] | [City] | [Dates]
- Dispensed medications for 100+ inpatients daily, maintaining 100% accuracy in medication orders
- Counseled patients on medication usage, side effects, and dietary interactions
- Conducted medication therapy reviews, identifying 8 potential drug interactions that were escalated to physicians
- Collaborated with clinical team on patient medication optimization
- Maintained controlled substance inventory and compliance with pharmacy regulations
- Managed pharmacy operations during night shift covering for 4 pharmacists
[If you have additional experience]:
Retail Pharmacist | [Pharmacy Name] | [City] | [Dates]
- Dispensed prescriptions with accuracy rate of 99.2%
- Provided patient counseling on OTC and prescription medications
- Managed pharmacy inventory and stock management
- Achieved 95% customer satisfaction rating
SKILLS
Clinical Knowledge: Drug interactions, medication therapy optimization, patient counseling, adverse drug reactions
Pharmacy Operations: Inventory management, POS systems, controlled substances management
Patient Care: Counseling, patient education, communication
Technical: EHR systems, pharmacy software, [other systems]
Bachelor of Pharmacy (B.Pharm) | [College Name] | [City] | [Year]
- Relevant coursework: Clinical Pharmacy, Pharmacology, Pharmaceutical Management
- [If strong GPA]: GPA: 3.5+/4.0
LANGUAGES
English: Fluent | Hindi: [Proficiency] | [Other languages]
STRENGTHS FOR PHARMACY ROLES
- Patient-focused approach to medication therapy
- Strong pharmaceutical knowledge
- Excellent communication and counseling skills
- Attention to detail and accuracy
- Compliance-oriented professional
Where to Find Pharmacy Jobs
Online Job Portals:
- Naukri.com – Search “Pharmacist” + city
- Indeed.com – Hospital, retail, pharmaceutical positions
- LinkedIn Jobs – Professional positions
- Glassdoor – Research company reviews
Direct Hospital Applications:
- Identify 20-30 hospitals in your city
- Find pharmacy department contact
- Email pharmacist CV with cover letter
Retail & Medical Store Chains:
- Apollo Pharmacy
- Medplus
- CVS & Wellness
- Local medical store chains
Pharmaceutical Companies:
- Major companies actively hire pharmacists for sales, quality, and regulatory roles
- Sun Pharma, Dr. Reddy’s, Cipla, Lupin, Glenmark
Recruitment Agencies:
- Healthcare recruitment specialists
- Pharmaceutical industry staffing agencies
- Can fast-track your applications
Interview Preparation
Common Pharmacy Interview Questions:
Q: “Why did you choose pharmacy as a career?”
Good Answer: “I’m drawn to the intersection of science and patient care. Pharmacy allows me to use my pharmaceutical knowledge to directly improve patient outcomes through medication education and therapy optimization. I find fulfillment in helping patients understand their medications and achieve better health through proper drug use.”
Q: “Describe a time you identified a medication error and how you handled it.”
Strategy: Show accountability and patient safety focus.
Good Answer: “During my hospital internship, I noticed a physician prescribed a medication to a patient with a documented allergy. I immediately consulted the patient record, verified the allergy, then contacted the prescribing physician. We discussed safer alternatives. The physician changed the prescription. This experience reinforced that pharmacists are the last safety check—it’s our responsibility to prevent medication errors that could harm patients.”
Q: “How do you handle pressure from patients or doctors regarding medications?”
Good Answer: “Healthcare involves difficult decisions. If a patient questions their medication, I explain the medication’s purpose, benefits, and side effects clearly. If a patient can’t afford their medication, I discuss generic alternatives or assistance programs. If a doctor prescribes something I have safety concerns about, I respectfully consult them professionally. My approach is always patient-centered with firm commitment to safety.”
Q: “What’s your experience with hospital pharmacy software?”
Be honest: “I have experience with [specific software from internship]. I’m a quick learner and have used multiple EHR systems during my training. I’m confident I can master your hospital’s systems quickly with training.”
Q: “Why should we hire you instead of other candidates?”
Good Answer: “I combine solid pharmaceutical knowledge from my B.Pharm education with practical internship experience. What sets me apart is my genuine passion for patient care and medication safety. During my internship, I received commendations for identifying medication discrepancies and communicating effectively with patients. I’m reliable, detail-oriented, and committed to continuous learning in this evolving field.”
Salary Negotiation for Fresh Pharmacy Graduates
When offered a position:
Research First:
- Check Glassdoor for similar roles at that organization
- Ask pharmacy seniors what entry-level pharmacists earn
- Know typical range (₹3-4 LPA for fresh B.Pharm graduates)
Negotiation Script:
“Thank you for the offer. I’m excited about joining [Hospital/Company] as a pharmacist. Based on my B.Pharm education, internship experience, and market research for entry-level pharmacists in [City], I was expecting ₹[X amount]. Would there be flexibility on the salary?”
What’s Negotiable:
- Base salary (10-15% room for entry-level)
- Performance bonus structure
- Professional development support
- Certification reimbursement (for CCP, specializations)
- Leave entitlements
If They Can’t Increase Salary:
“I understand. Would you be able to support my professional development? For example, would the organization sponsor my CCP certification after my first year?”
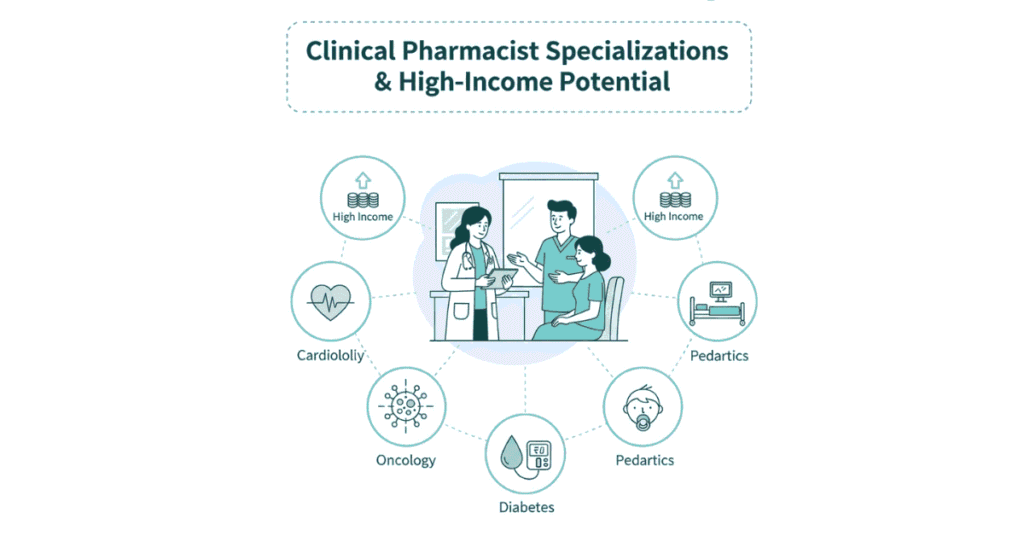
Clinical Pharmacy Specialization: Where Pharmacy is Evolving
Clinical pharmacy deserves special attention because it’s where modern pharmacy is heading.
What is Clinical Pharmacy?
Clinical pharmacy goes beyond dispensing. Clinical pharmacists:
- Conduct comprehensive medication therapy reviews
- Make recommendations to optimize patient treatment
- Manage specific disease states (hypertension, diabetes, cancer, etc.)
- Participate in clinical rounds with doctors
- Educate patients about complex medication regimens
- Monitor for adverse effects and interactions
- Work as part of interdisciplinary healthcare teams
The Key Difference: Retail pharmacists dispense what doctors prescribe. Clinical pharmacists help doctors make better prescribing decisions.
Specialization Areas
- Cardiology Pharmacy
- Manages heart disease medications
- Specialization in anticoagulants, antiarrhythmics, ACE inhibitors
- Salary: ₹10-15 LPA (specialized)
- Demand: High
- Oncology Pharmacy
- Specializes in cancer medications (chemotherapy, targeted therapy)
- Complex dose calculations
- Managing severe side effects
- Salary: ₹10-16 LPA
- Demand: Very High (growing field)
- Diabetes & Endocrinology
- Manages diabetes, thyroid, hormone medications
- Patient education critical
- Salary: ₹9-13 LPA
- Demand: High (pandemic increased diabetes)
- Critical Care Pharmacy
- Manages ICU medications
- Complex drug interactions
- Emergency decision-making
- Salary: ₹10-14 LPA
- Demand: High
- Psychiatry Pharmacy
- Specializes in psychiatric medications
- Mental health expertise
- Salary: ₹8-12 LPA
- Demand: Growing
- Pediatric Pharmacy
- Specializes in children’s medications
- Dose adjustments for age
- Salary: ₹9-13 LPA
- Demand: Growing
How to Specialize in Clinical Pharmacy
Path:
- Year 1-2: Work as hospital pharmacist (general)
- Year 2-3: Get M.Pharm in Clinical Pharmacy (2 years)
- Year 4+: Work as clinical pharmacist in your specialty
- Year 5-7: Get CCP (Certified Clinical Pharmacist) certification
- Year 7+: Senior clinical pharmacist, potential leadership
Timeline to ₹10+ LPA: Typically 4-6 years with M.Pharm pursuit
Worth It? Absolutely. Clinical pharmacists are highly valued, well-paid, and genuinely impact patient outcomes
See how it works? Diagnosis codes say “what’s wrong,” procedure codes say “what was done,” and HCPCS codes say “what equipment/supplies were used.” All three work together to paint a complete picture of the patient visit.
Common Pharmacy Career Mistakes: Learn From Others
Mistake 1: Staying in Retail Without Strategy
Many pharmacy graduates spend 5-10 years in retail with no career progression. Then they wonder why they’re still earning ₹4-5 LPA while peers earn ₹10+.
Instead: Retail is fine initially (experience, earning money). But within 1-2 years, make strategic moves:
- Transition to hospital (better salary, learning)
- Get specialized certification
- Move to pharmaceutical company
- Work toward opening own pharmacy with clear business plan
Mistake 2: Not Getting Advanced Qualifications
Some pharmacists think B.Pharm is enough forever. Then they plateau at ₹6-8 LPA while M.Pharm holders advance to ₹12-15+ LPA.
Instead: Evaluate M.Pharm within first 2 years. If career growth is your goal, pursue it.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Specialization
General pharmacists are common. Specialized pharmacists (oncology, cardiology, clinical) are rare and paid significantly more.
Instead: After 1-2 years, choose a specialization. Become expert in that area.
Mistake 4: Poor Communication Skills
Some pharmacists are technically excellent but terrible at explaining medications to patients. This limits career growth and patient satisfaction.
Instead: Actively develop communication skills:
- Practice patient counseling
- Join communication workshops
- Learn to explain complex concepts simply
- Develop comfort with public speaking
Mistake 5: Not Networking
Some pharmacists work in isolation, missing career opportunities through professional networks.
Instead:
- Join pharmacy professional associations
- Attend pharmacy conferences
- Network with hospital directors and senior pharmacists
- Maintain relationships with previous colleagues
Mistake 6: Switching Jobs Too Frequently
Some pharmacists change jobs every 1-2 years chasing small salary increases. Employers see this as red flag.
Instead: Stay 2-3 years minimum in each role. Make strategic job changes for significant advancement (₹1-2 LPA jump), not small increases (₹20,000).
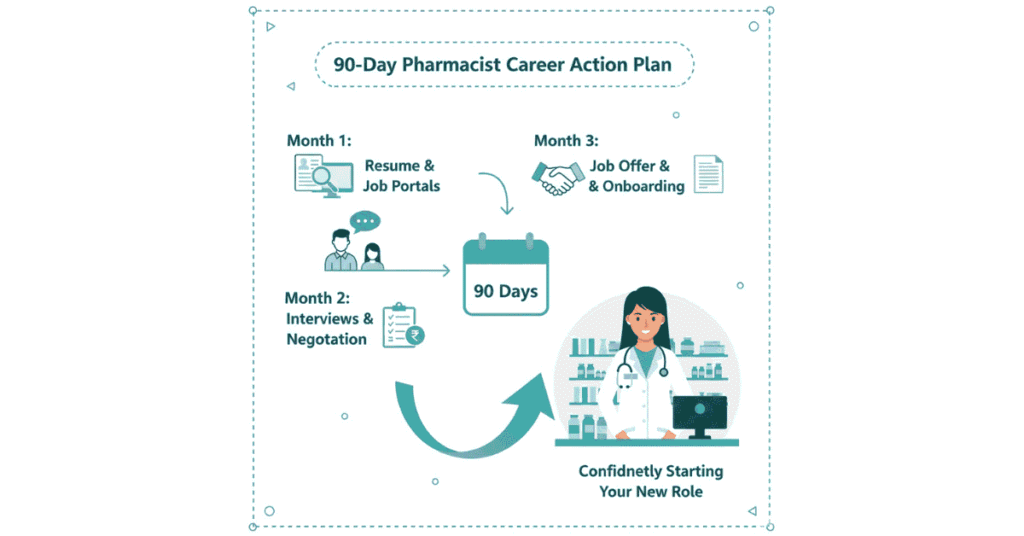
Your 90-Day Action Plan: From Pharmacy Graduate to Employed Pharmacist
Month 1: Foundation & Applications (Days 1-30)
Week 1:
- ☐ Finalize B.Pharm degree/complete internship
- ☐ Register as pharmacist with state licensing authority
- ☐ Create professional resume using template provided
- ☐ Create LinkedIn profile (mark “Open to Pharmacist Opportunities”)
Week 2:
- ☐ Identify 15-20 target hospitals in your city
- ☐ Create list of pharmaceutical companies hiring pharmacists
- ☐ Research medical store chains and retail positions
- ☐ Connect with pharmacy professionals on LinkedIn
Week 3:
- ☐ Apply to 10-15 hospital pharmacist positions
- ☐ Apply to 5-10 pharmaceutical company positions
- ☐ Apply to 5-10 retail pharmacy positions
- ☐ Prepare interview answers to common questions
Week 4:
- ☐ Send direct applications to hospitals (email pharmacy heads)
- ☐ Apply to 10 more positions
- ☐ Research pharmacist specializations you’re interested in
- ☐ Join pharmacy professional groups on LinkedIn/Facebook
End of Month 1: 30-40+ applications submitted, LinkedIn connections growing, interview prep underway
Month 2: Interviews & Offers (Days 31-60)
Week 5:
- ☐ Interviews starting (likely by now)
- ☐ Practice case studies related to pharmacy
- ☐ Apply to 10 more positions
- ☐ Follow up on previous applications
Week 6:
- ☐ Attend interviews (2-5 expected by now)
- ☐ Send thank-you emails after interviews
- ☐ Continue applications (5-10 more)
- ☐ Research company culture of organizations interviewing you
Week 7:
- ☐ More interviews happening
- ☐ Get feedback if rejected (what to improve)
- ☐ Apply to 5-10 final positions
- ☐ Prepare for negotiation if offers come
Week 8:
- ☐ Receive job offer (likely by now)
- ☐ Negotiate salary if applicable
- ☐ Complete offer acceptance
- ☐ Prepare joining documents
End of Month 2: 50-60+ applications submitted, 3-6 interviews completed, 1-2 job offers received
Month 3: Starting Your Pharmacy Career (Days 61-90)
Week 9:
- ☐ Complete joining formalities
- ☐ Get employee ID and credentials
- ☐ Complete orientation
- ☐ Meet your pharmacy team
Week 10:
- ☐ Start your first day as pharmacist!
- ☐ Learn pharmacy systems and operations
- ☐ Shadow experienced pharmacists
- ☐ Ask questions constantly
Week 11:
- ☐ Start dispensing and patient counseling
- ☐ Build relationships with colleagues
- ☐ Get feedback on your performance
- ☐ Observe and learn specializations
Week 12:
- ☐ Complete first month of employment
- ☐ Reflect on role and performance
- ☐ Plan next steps (specialization? M.Pharm? certifications?)
- ☐ Celebrate your pharmacy career launch!
End of Month 3: First pharmacist job secured, earning, learning, building career!
Closing: Your Pharmacy Career in Healthcare
You’ve reached the end of this guide. You now understand pharmacy as a complete profession—far beyond the retail counter image most people have.
Here’s what’s possible with pharmacy:
- Quick employment: Direct jobs after B.Pharm (no further studies required)
- Decent starting income: ₹2.5-4 LPA right after graduation
- Clear growth: ₹15-25 LPA within 10 years with strategic moves
- Multiple paths: Clinical, research, sales, management, entrepreneurship
- Real patient impact: Direct influence on healthcare outcomes
- Job security: Healthcare always needs pharmacists
- Specialization potential: Become expert in specific disease areas, earn premium
Pharmacy isn’t just pills and potions. It’s science, patient care, business, and healthcare innovation combined.
Whether you choose retail initially, hospital pharmacy, specialization in clinical roles, or pharmaceutical industry—pharmacy offers genuine career flexibility and growth.
Your pharmacy career doesn’t start someday. It starts when you accept that first job.
Good luck, future pharmacist. The healthcare system needs your pharmaceutical expertise and patient-focused care. 💊✨
