Medical Coding Career – Your Complete Roadmap
Table of Contents
Introduction: The Hidden Healthcare Career That Pays Well Without Patient Contact
Imagine this: You’re sitting at your desk in a comfortable air-conditioned office. No hospital smell. No patient emergencies. No shift work. Your job? Converting doctor’s notes and patient information into standardized codes that determine hospital billing and insurance claims. You work on a typical 9-to-5 schedule. Your accuracy directly impacts hospital revenue. And here’s the best part—you don’t need a medical degree to do this job.
This is medical coding. And it’s one of the most underrated, accessible healthcare careers in India that pays surprisingly well.
Most people don’t even know this career exists. They hear “healthcare career” and think doctors or nurses. But hospitals and insurance companies need medical coders desperately. Every single patient record needs coding. Every diagnosis needs documentation. Every procedure needs classification. That’s where coders come in.
Here’s what makes medical coding special:
- No medical background required. You can come from commerce, arts, or any educational background. Some of the best coders I know studied commerce in 12th grade.
- Quick entry. 3-6 months of training gets you job-ready. Compare that to nursing (2-4 years) or medicine (5.5 years).
- Decent starting salary. Fresh medical coders typically earn ₹2-3 LPA, which is competitive given the quick entry.
- Significant growth potential. Within 10 years, experienced coders managing teams or doing specialized coding earn ₹15-25 LPA.
- Remote work opportunities. Work from home jobs are abundant in medical coding. Many Indian coders work for US hospitals remotely, earning significantly more.
- International earning potential. The global medical coding job market is huge. Remote positions for international clients can pay ₹25-40 LPA from India itself.
- Job security. Healthcare billing isn’t going anywhere. As long as hospitals exist, they need coders.
If you’re looking for a healthcare career that doesn’t require 5+ years of education, doesn’t involve patient contact if you don’t want it, offers good pay and clear growth, and has abundant remote work opportunities—medical coding might be exactly what you’re searching for
What is Medical Coding?
Before diving into career strategy, let’s understand what medical coding actually is, because honestly, most people have no clue.
The Simple Version
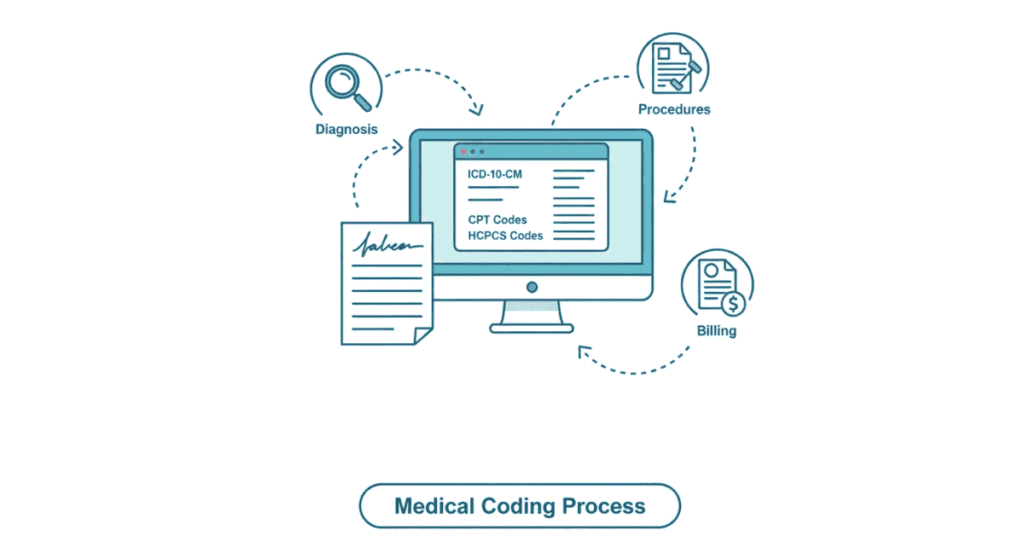
Every time a patient visits a doctor, a diagnosis is made, and treatments are provided. The doctor writes all this down in patient notes. But here’s the problem: these notes are written in human language. Insurance companies, hospital billing departments, and government agencies need standardized information to process payments, maintain records, and analyze health trends.
Enter: Medical coders. Your job is to read the doctor’s notes and convert all that information into standardized codes. It’s like translating medical information into a universal language that hospitals, insurance companies, and government agencies all understand.
The Real Example
Let’s say a 45-year-old man visits his doctor with high blood pressure. The doctor examines him, runs tests, prescribes medications, and writes detailed notes. Now the hospital billing department needs to know:
- What was his diagnosis? (Medical condition)
- What procedures were done? (Tests, examinations)
- What medications were given? (Treatment)
- What did the visit cost? (For billing insurance)
You, as a medical coder, read those doctor’s notes and assign:
- ICD-10 code: A standardized diagnosis code (e.g., I10 for Essential Hypertension)
- CPT code: Procedure code for what the doctor did (e.g., 99213 for Office visit, established patient)
- HCPCS code: Equipment or supplies used (if applicable)
These codes get submitted to the insurance company, which then pays the hospital based on the codes. Accuracy matters because wrong codes mean wrong reimbursement. Hospital loses money. Insurance company denies legitimate claims. This is why medical coders are so important.
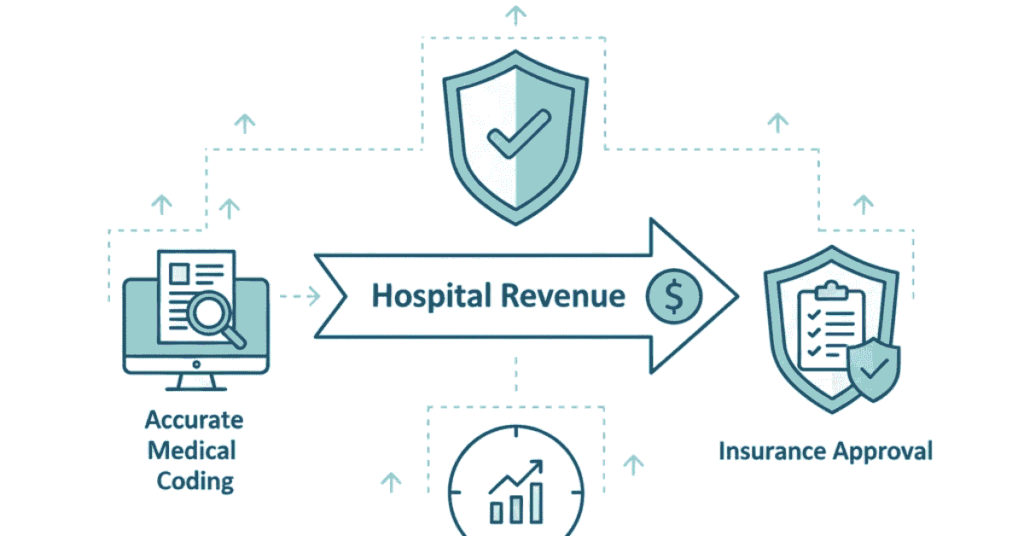
Why Hospitals Need Medical Coders
Financial Survival:
Hospitals operate on thin margins. A large hospital might process 500-1000 patient records daily. Wrong coding even 2-3% of the time means significant revenue loss. For a hospital earning ₹100 crores annually, a 2% coding error could mean ₹2 crores in lost revenue
Insurance Compliance:
Insurance companies audit medical records. Incorrect coding is considered fraud (whether intentional or not). Hospitals face legal penalties, reputation damage, and claim denials. Accurate medical coders protect hospitals from these risks.
Healthcare Analytics:
Government and healthcare planners use coding data to understand disease patterns, treatment effectiveness, and health trends. Accurate coding contributes to better public health planning.
Operational Excellence:
Medical codes are used for resource planning, equipment procurement, staffing decisions, and departmental budgeting. Accurate coding leads to better operational decisions.
This is why hospitals increasingly hire dedicated medical coders and don’t rely on doctors or nurses to handle coding. It requires specialized knowledge and is too important for accuracy to be an afterthought
Do You Need a Medical Background? The Honest Truth
Here’s where medical coding becomes attractive for non-medical background students: You absolutely do not need a medical background to become a medical coder.unicode+1
Let me be specific: I’m talking about ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems. These are systematic, rule-based classification systems. They’re not like medicine where you need years of clinical judgment training. They’re more like accounting or filing systems where you learn rules and apply them.
What You Actually Need to Know
Medical Terminology:
Yes, you’ll need to learn medical terms. But here’s the thing—you don’t need to understand the medicine behind it. You just need to recognize terms and know which codes they map to.
Example: You see “myocardial infarction” in a doctor’s note. You don’t need to understand what happens in the heart during an MI. You just need to know that “MI” = “Heart attack” and know the correct ICD-10 code for it.
How to Learn Terminology:
- Online courses (Udemy, Coursera) teach medical terminology in 2-4 weeks
- Medical coding training programs include comprehensive terminology teaching
- Most terminology is learned through practice (you’ll recognize patterns after 50-100 charts)
The Coding Systems:
ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS are systems with rules. You learn the rules, apply them to patient records, and you’re coding. No clinical judgment required.
Who Becomes a Medical Coder?
Commerce students: Many coders have commerce background. Coding is systematic like accounting—rules, classification, accuracy required. They transition easily.
Arts students: Some coders studied humanities. They often have strong language skills, which helps in understanding medical documentation.unicode
Engineering students: Technical background helps with coding logic and systematic thinking.
Non-traditional backgrounds: Some coders come from completely different fields. What matters is accuracy, attention to detail, and willingness to learn.
The One Thing You Must Have
More important than medical background: Accuracy mindset.
Medical coding isn’t creative. You can’t “interpret” what codes fit. Codes are either right or wrong. This requires:
- Attention to detail (noticing small but important information in doctor’s notes)
- Patience (carefully reading entire documents before coding)
- Perseverance (looking up correct codes even if it takes time)
- Accountability (accepting that your error = hospital loss)
If you’re the type who skims text quickly, guesses answers, or doesn’t double-check work, medical coding will frustrate you. If you’re detail-oriented, thorough, and take pride in accuracy, you’ll thrive
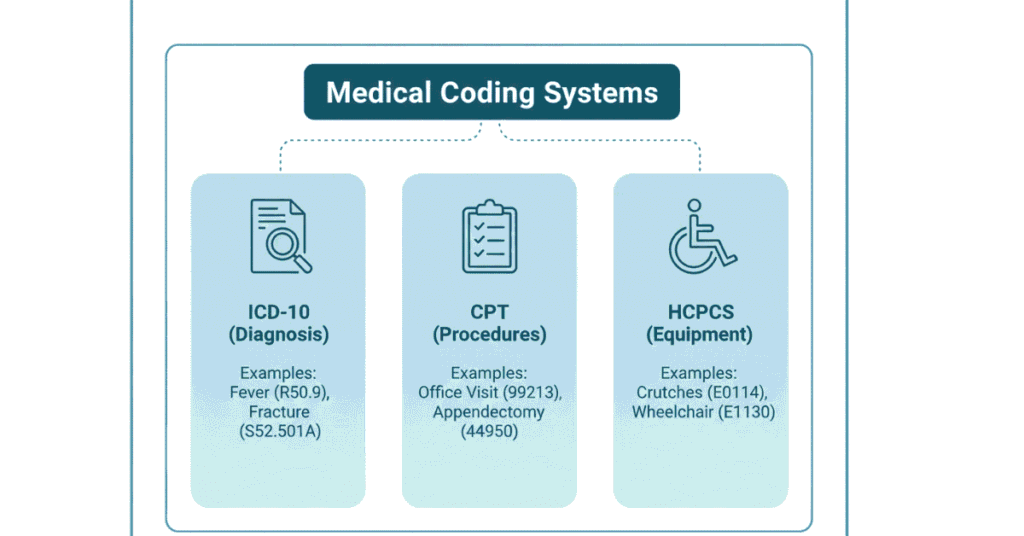
The Three Coding Systems Explained Simply: ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS
Understanding these three systems is fundamental. Let’s break down each one without overwhelming you.
ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision):
What It Is:
ICD-10 is a standardized system of diagnosis codes. Every disease, condition, symptom, and health issue gets a unique code. Think of it as a massive medical dictionary where each condition has a code number.
Why It Exists:
Insurance companies, hospitals, and governments need to track what diseases people have. If they just had text descriptions, different doctors might write it differently. “High blood pressure,” “hypertension,” “BP up”—all mean the same thing, but they’re different text descriptions. ICD-10 codes standardize this. The code “I10” means “Essential Hypertension” everywhere, every time
Code Structure:
ICD-10 codes have 3-7 characters. They look like: E11.9 (Type 2 Diabetes without complications), I10 (Essential Hypertension), M54.5 (Low back pain).
Real Examples:
- Patient has Type 2 Diabetes → Code: E11.9
- Patient has asthma → Code: J45.909
- Patient has high blood pressure → Code: I10
- Patient complains of headache → Code: G89.29
Your Job with ICD-10:
Read the doctor’s notes. Find the diagnosis. Assign the correct ICD-10 code. That’s it.
How Many Codes Are There?
Thousands. Around 68,000+ ICD-10-CM codes exist. Don’t panic—you won’t memorize them. You’ll use reference books and software databases that help you find the right code.annexmed
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology):
What It Is:
While ICD-10 codes describe “what’s wrong with the patient,” CPT codes describe “what did the doctor do about it?” CPT codes identify procedures, services, and test
Why It Exists:
Insurance needs to know not just the diagnosis but what treatment was provided. If a patient had high blood pressure, did the doctor just check it? Or did they run tests, prescribe medications, have follow-up visits? CPT codes communicate this.
Code Structure:
CPT codes are 5-digit numbers. They look like: 99213 (Office visit), 36415 (Venipuncture—drawing blood), 70553 (MRI of brain).
Real Examples:
- Doctor’s office visit (established patient) → Code: 99213
- Lab test: Blood draw → Code: 36415
- Imaging: MRI of brain → Code: 70553
- Imaging: Chest X-ray → Code: 71046
Your Job with CPT:
Read what procedures or services the doctor performed. Assign the correct CPT code for each service.
HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System):
What It Is:
HCPCS codes describe equipment, supplies, and services not covered by CPT codes. If a patient received a wheelchair, bandages, medications by injection, or ambulance services—HCPCS codes classify these.
Code Structure:
HCPCS codes start with a letter followed by 4 numbers. They look like: E0607 (Home blood glucose monitor), J7507 (Medication by IV injection), L3010 (Foot orthotic device).
Real Examples:
- Wheelchair → Code: E0601
- Diabetes test strips → Code: A4253
- Medication by IV → Code: J codes (various)
- Ambulance transport → Code: A0429
Your Job with HCPCS:
Identify equipment and supplies provided to the patient. Assign appropriate HCPCS codes.
How These Three Work Together
Here’s a complete example to show how all three systems work:
Patient Case: 55-year-old diabetic patient visits hospital for chest pain evaluation.
Doctor’s Notes:
- Chief complaint: Chest pain
- Diagnosis: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Angina (chest pain from heart condition)
- Procedures: ECG (heart test), blood draw for cardiac enzymes, chest X-rayTreatment: Given oxygen, IV medication for chest pain
- Equipment: Applied continuous cardiac monitoring
- Supplies: Given nitroglycerin medication
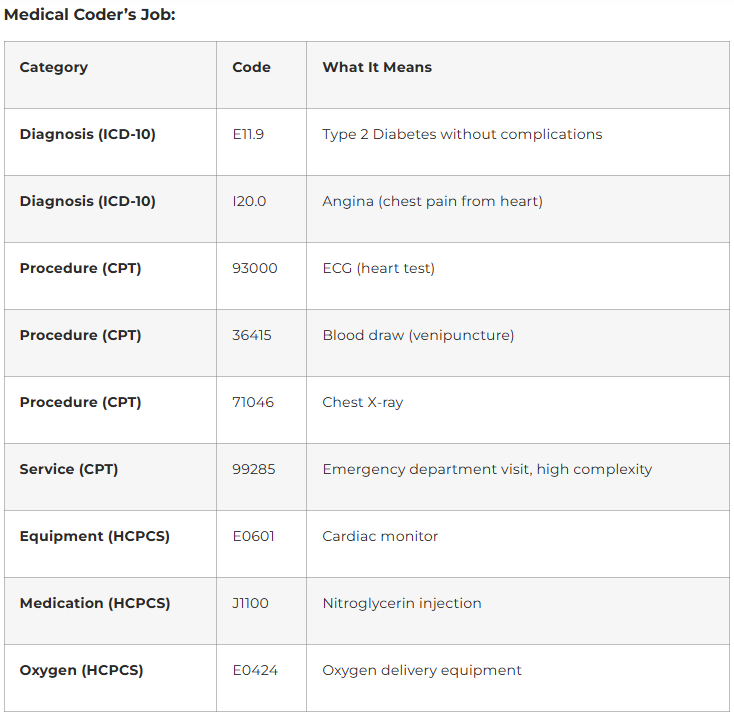
See how it works? Diagnosis codes say “what’s wrong,” procedure codes say “what was done,” and HCPCS codes say “what equipment/supplies were used.” All three work together to paint a complete picture of the patient visit.
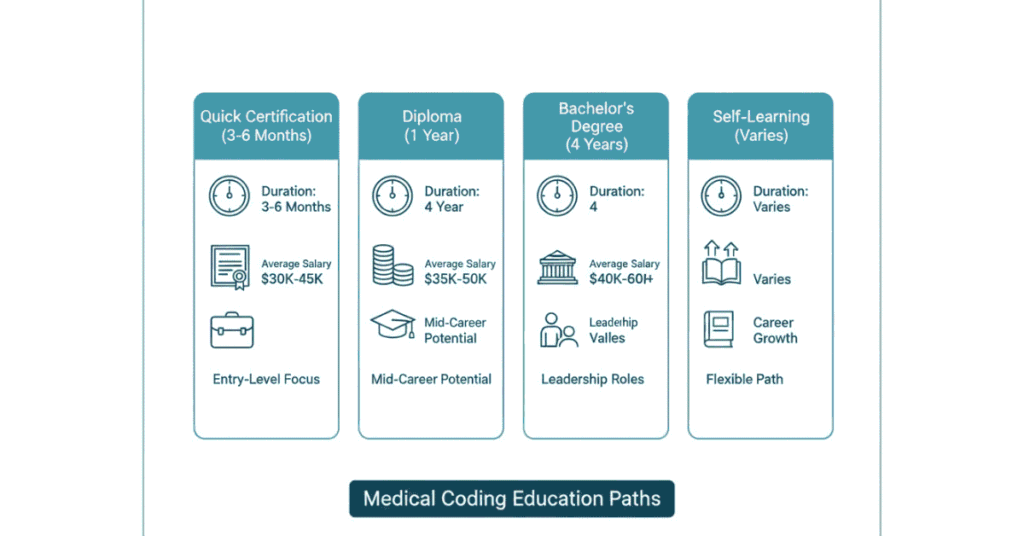
Medical Coding Career Pathways: Which Route Gets You Hired Fastest?
Pathway 1: Quick Certification Program (3-6 Months) – Fastest Entry
What It Is:
Short-term, focused training programs that teach you ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems. These programs prioritize practical skills over theory.
Duration: 3-6 months (some intensive programs as short as 12 weeks)
Cost: ₹15,000-50,000 depending on institute quality
What You’ll Learn:
- Medical terminology (basics)
- ICD-10 coding system in detail
- CPT coding system in detail
- HCPCS coding system
- Practice with real medical records
- Exam preparation (if pursuing CPC certification)
Who Should Choose This:
- You want to start earning quickly
- You’re already working and need part-time/weekend training
- You want to test if medical coding interests you before deeper investment
- You’re motivated by quick employment
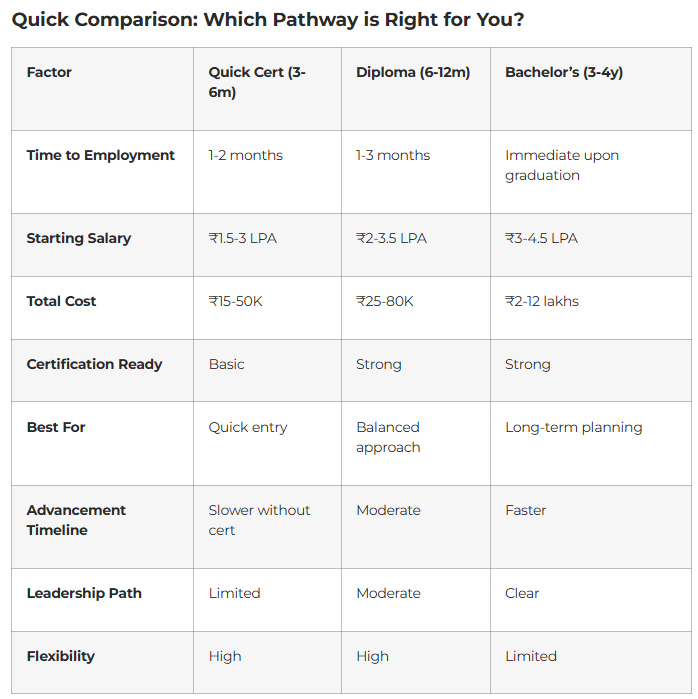
Employment Timeline: Can get entry-level job within 1-2 months after completion
Salary Expectation: ₹1.5-3 LPA starting
Best For: Quick entry into workforce, testing career fit, earning while building skills
Challenges:
- Without certification, advancement is slower
- Employers may prefer certified coders
- Knowledge might be surface-level
Pathway 2: Diploma Program (6-12 Months) – The Comprehensive Path
What It Is:
More comprehensive training programs that combine coding system education with healthcare billing, compliance, and practical case studies. These programs often prepare you for certification exams.
Duration: 6-12 months
Cost: ₹25,000-80,000
What You’ll Learn:
- Medical terminology (comprehensive)
- Healthcare billing fundamentals
- ICD-10 coding systems
- CPT coding systems
- HCPCS coding systems
- Compliance and regulations
- Quality assurance in coding
- Real-world case studies (100+ practice charts)
- CPC or CCS certification exam preparation
Who Should Choose This:
- You want thorough knowledge before working
- You’re planning to pursue certification (better preparation)
- You want to understand healthcare billing context
- You have 6-12 months available for training
Employment Timeline: 1-3 months after completion with good preparation
Salary Expectation: ₹2-3.5 LPA starting
Best For: Career building, certification preparation, comprehensive understanding
Advantages:
- Better knowledge retention
- Good CPC exam preparation
- Understand healthcare billing system
- More job-ready after completion
Pathway 3: Bachelor’s Degree in Health Information Management (3-4 Years) – The Professional Route
What It Is:
Full 3-4 year bachelor’s degree program covering health information, medical coding, healthcare IT, management, and compliance.
Duration: 3-4 years
Cost: ₹2-5 lakhs total (government colleges) or ₹4-12 lakhs (private colleges)
What You’ll Learn:
- Comprehensive healthcare management
- Medical coding systems (ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS)
- Health information systems and databases
- Healthcare laws and compliance
- Management and leadership basics
- Healthcare analytics
- Research methodology
- Business aspects of healthcare
Who Should Choose This:
- You want management/leadership roles
- You have time for 3-4 year investment
- You want maximum career flexibility
- You might move into healthcare administration later
Employment Timeline: Immediately upon graduation (4-week job search typical)
Salary Expectation: ₹3-4.5 LPA starting
Best For: Long-term career planning, leadership aspirations, maximum career flexibility
Advantages:
- Bachelor’s degree credential (universally valued)
- Deep healthcare knowledge
- Leadership pathway immediately available
- Better positioning for international opportunities
Limitations:
- 3-4 year time investment
- Significant financial investment
- Takes longer to start earning
Pathway 4: Self-Taught with Online Courses (3-6 Months) – The Budget Option
What It Is:
Learning through Udemy, Coursera, YouTube, and practice on your own. Not recommended as primary learning method, but can work for highly motivated individuals.
Duration: 3-6 months (depending on discipline)
Cost: ₹500-5,000 (very affordable)
Pros:
- Extremely affordable
- Learn at your own pace
- Flexibility for working professionals
Cons:
- Lack of structure and guidance
- Difficult to get practice charts reviewed
- No certification preparation support
- Higher risk of not learning correctly
- Harder to get hired without formal training
Recommendation: This works ONLY if combined with formal training or if you already have strong technical background in similar systems.
My Recommendation: If you want to START WORKING and EARNING within 3 months while pursuing certification later, choose the quick certification program. If you want to be thoroughly prepared and potentially fast-track to senior roles, choose the diploma.
CPC Certification: Your Golden Ticket to Better Salary
Now let’s talk about what can genuinely increase your earning potential: CPC (Certified Professional Coder) certification.
What is CPC Certification?
CPC stands for Certified Professional Coder. It’s an industry-recognized certification issued by AAPC (American Association of Professional Coders). It validates that you understand medical coding systems and can apply them correctly.medesunglobal+2
Think of it like this: A medical coding certificate from a training institute says “I learned medical coding.” CPC certification says “I learned it well enough to pass a rigorous national exam and I meet AAPC standards.”
Why CPC Certification Matters
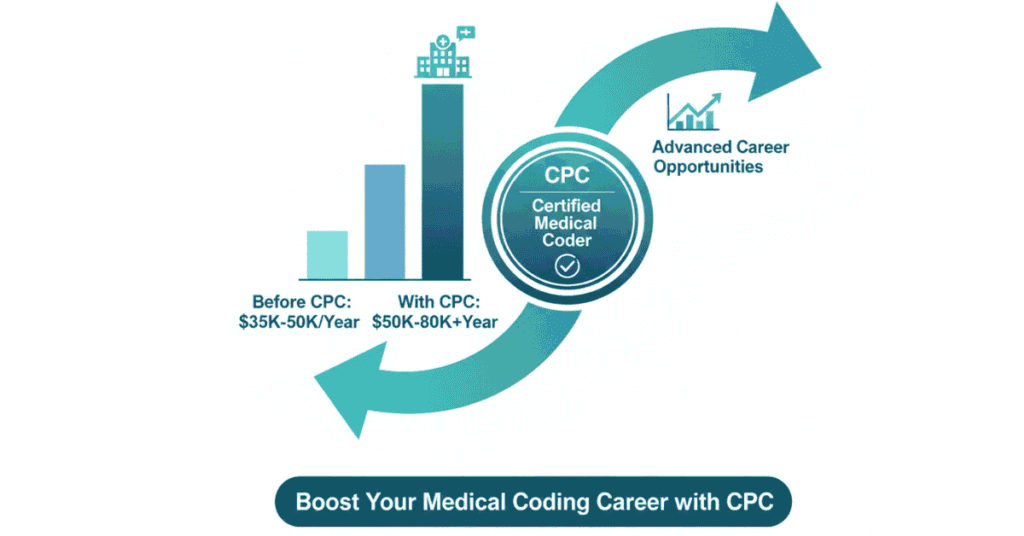
Salary Impact: The most important part—CPC certification increases your salary by 20-30%.
Comparison:
- Medical coder without CPC: ₹2-2.5 LPA starting
- CPC-certified coder: ₹2.5-3.5 LPA starting
Over a 10-year career, this 20-30% difference adds up to several lakhs more in total earnings.
Employer Preference: Most reputable hospitals, BPOs, and international clients PREFER or REQUIRE CPC certification for better positions. Non-certified coders are often stuck in entry-level roles.
International Opportunities: If you want to work remotely for international clients earning premium rates (₹25-40 LPA from India), CPC certification is almost mandatory.
Career Advancement: Moving from coder to senior coder, auditor, or manager is much easier with CPC. Without it, advancement is limited.
CPC Exam Details
Exam Format:
- Computer-based test (CBT)
- 150 multiple choice questions
- 5 hours total duration
- Questions test ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS coding knowledge
Pass Score:
You need 70% score (105 out of 150 questions) to pass.
Difficulty Level:
CPC exam is genuinely challenging. First-time pass rate is roughly 50-60%. This is intentional—AAPC wants only truly competent coders to hold the CPC credential.
Exam Cost:
- AAPC membership + exam: ₹20,000-30,000 total
- Available in India through authorized testing centers
How to Prepare for CPC Exam
Study Timeline:
Typically 4-8 weeks of dedicated study for people with 6-12 months of coding experience. If you’re starting fresh, add another 2-4 weeks of coding fundamentals.cigmamedicalcoding
Study Strategy:
- Weeks 1-2: Strengthen fundamentals using AAPC official resources
- Weeks 2-4: Deep dive into ICD-10 and CPT systems
- Week 5: Practice exams (identifying weak areas)
- Weeks 5-7: Focused study on weak topics
- Week 8: Final practice exams and review
Pass Tips:
- Invest in AAPC official study materials (not pirated content)
- Take multiple practice exams (important!)
- Study with real medical records (not just theory)
- Join study groups (finding peers preparing for CPC helps)
- Time management practice (exam has time pressure)
- Don’t just memorize codes—understand the logic
If You Fail:
Don’t panic. About 40-50% of first-time takers don’t pass. You get detailed feedback on weak areas. Most people pass on their second or third attempt. Take time to address identified weaknesses and retake.
Other Valuable Certifications
Beyond CPC, other certifications increase your value:
CCS (Certified Coding Specialist):
Similar to CPC but focuses specifically on hospital inpatient coding. For coders working in hospital billing departments.
RHIT (Registered Health Information Technician):
Broader than CPC. Covers health information systems, not just coding.
CEMC (Certified Encounter Management Coder):
Focuses on outpatient/ambulatory coding.
Specialization Certifications:
- CRC (Certified Risk Adjustment Coder)
- Specialty coding (cardiovascular, orthopedic, etc.)
But CPC is the most valuable and recognized. Get that first.
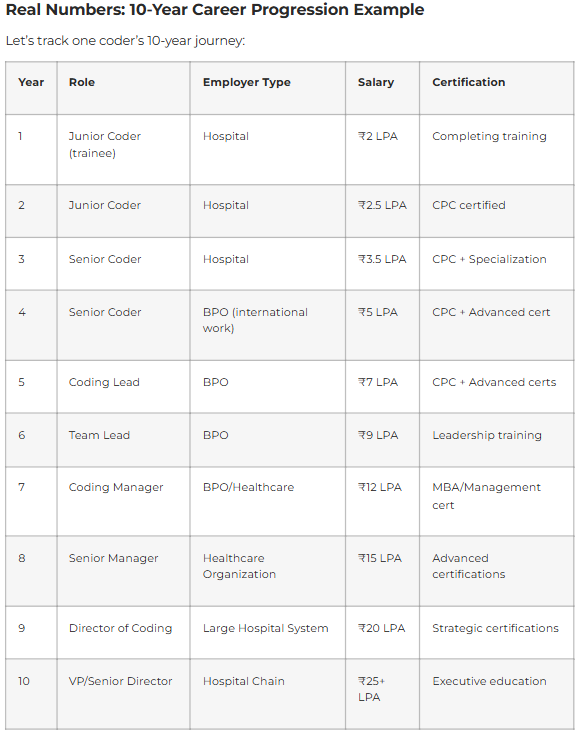
Medical Coder Salary & Career Progression: Realistically
Entry Level (0-1 Years): Trainee/Junior Medical Coder
Typical Responsibilities:
- Learning medical coding fundamentals
- Coding 30-50 charts per day (starting slow)
- Working under supervision
- Accuracy around 90-95% (acceptable as trainee)
- Asking lots of questions (expected at this level)
Salary Range: ₹1.5-2.5 LPA (₹12,500-20,000/month)
Location Variation:
- Tier 1 cities (Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore): ₹2-2.5 LPA
- Tier 2 cities: ₹1.5-2 LPA
- Small cities/towns: ₹1.2-1.5 LPA
What You Should Focus On:
- Build speed and accuracy (both matter)
- Get CPC certification if not done
- Learn hospital’s specific processes
- Understand common diagnoses in your hospital
- Build relationships with supervisors
Common Issues:
- Job feels repetitive (it is initially)
- Pressure about accuracy (normal—healthcare coding is high-stakes)
- Work hours feel long (learning curve makes things take longer)
How to Overcome: Remember, this is investment period. Within 1-2 years you’ll gain speed and this changes dramatically.
Junior Coder (1-2 Years): Certified Coder
Key Achievement: By now you should have CPC certification (if not, get it ASAP)
Typical Responsibilities:
- Coding 60-80 charts daily independently
- 97%+ accuracy expected
- Mentoring newly hired trainees
- Handling specialty coding (complex cases)
- Training on new coding guidelines (yearly updates)
Salary Range: ₹2.5-3.5 LPA (₹20,000-30,000/month)
With CPC Certification: You should be in the ₹2.5-3.5 LPA range. Without it, advancement slows.
What to Focus On:
- Maintain 98%+ accuracy consistently
- Specialize in one department (cardiology, orthopedics, etc.)
- Learn quality assurance basics
- Take on training responsibilities
- Consider auditing (checking other coders’ work)
Career Decisions:
- Stay in hospital coding (stable, steady advancement)
- Transition to BPO/International clients (higher pay, remote possible)
- Move toward audit/QA roles (supervisory track)
Mid-Career (2-5 Years): Senior Coder or Auditor
Typical Responsibilities (as Senior Coder):
- Coding 80-100+ charts daily
- Handling most complex cases in hospital
- Training junior coders
- Quality assurance for junior staff
- Working with doctors to clarify diagnoses
Typical Responsibilities (as Auditor):
- Reviewing other coders’ work (5-10% audit rate standard)
- Identifying errors and retraining coders
- Generating compliance reports
- Suggesting process improvements
Salary Range:
- Senior Coder: ₹3.5-5.5 LPA (₹30,000-45,000/month)
- Auditor: ₹4-6.5 LPA (₹35,000-55,000/month)
Career Split Point:
By now you choose direction:
- Technical Track: Become specialized coder (cardiology coding, oncology coding, etc.) earning ₹4-6 LPA
- Supervisory Track: Move toward QA/auditing roles earning ₹4.5-7 LPA
- International Track: Work for international clients remotely earning ₹8-15 LPA equivalent
What to Focus On:
- Specialization in specific coding are
- Advanced certifications (CCS, specialization certs)
- Leadership development if supervisory track
- Remote opportunities if internationalization preferred
Senior Level (5-8 Years): Coding Manager/Lead
Typical Responsibilities:
- Managing team of 3-10 coders
- Performance reviews and staff development
- Compliance and audit oversight
- Process improvements
- Client management (if handling external clients)
- Training on new coding guidelines
Salary Range: ₹8-15 LPA (₹65,000-1,25,000/month)
Benefits Often Include:
- Performance bonuses
- Flexible work arrangements
- Remote work options
- Professional development budget
Advancement Requirements:
- Proven team leadership
- Excellence in coding (technical knowledge)
- Communication skills
- Problem-solving mindset
- Often: MBA or additional management certification
Expert Level (8-12+ Years): Director/Senior Manager
Typical Responsibilities:
- Overseeing entire coding department (50+ coders)
- Strategy for coding operations
- Cost optimization and revenue maximization
- Compliance and regulatory matters
- New technology implementation
- Vendor management
Salary Range: ₹15-25+ LPA (₹1,25,000-2,00,000+/month)
Who Reaches Here:
- Consistently excellent performers (top 5-10% of coders)
- Strong leadership skills
- Advanced education (MBA or equivalent)
- Proactive problem-solvers
Good communication across organizational levels
Remote Medical Coding: Earn ₹25-40 LPA from Your Home
The International Medical Coding Opportunity
The United States has a massive shortage of medical coders. US hospitals, insurance companies, and billing companies actively hire coders from India to code US medical records.remote
From your home in India, you code medical records for US hospitals. You earn in USD (typically $12-25 per hour depending on experience and complexity). At current exchange rates, this translates to ₹1,000-2,000+ per hour, or ₹20,000-40,000+ per day if you’re working 8-10 hours.remote
Why This Opportunity Exists
Labor Shortage: USA has fewer coders than jobs available. They must hire internationally.
Cost Efficiency: Even paying Indian coders $12-15/hour is cheaper for US hospitals than hiring US-based coders (who earn $40-60/hour).remote
Time Zone Advantage: India being opposite time zone from USA means work can happen 24/7. When US offices close, Indian coders take over.
English Proficiency: Indian coders speak English fluently, making remote collaboration easy.
Quality: Indian coders trained by AAPC standards are as competent as US coders, sometimes better due to higher competition.
How Remote International Coding Works
Employer Types:
Direct hospital employment: Work directly forUS hospital (benefits, salary, stability)
Outsourcing companies: Work for Indian BPOs contracted to US hospitals (more jobs available, flexibility)
Independent contractor: Freelance for multiple clients (highest earning potential, most variable income)
Typical Work Model:
You receive access to patient medical records digitally
You code them using ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS
You submit coded records to company
You’re paid per chart coded (piecewise) or hourly
Payment Models:
Per chart: ₹100-500 per chart depending on complexity (fast coders earn ₹20,000-30,000/day)
Hourly: $12-25/hour = ₹1,000-2,000/hour = ₹8,000-16,000/day
Monthly salary: Some employers offer fixed salary (rare for beginners, common for experienced)
Example: An experienced medical coder codes 30-40 charts per day at ₹200/chart = ₹6,000-8,000/day = ₹1.5-2 LPA/month = ₹18-24 LPA/year
Requirements for Remote International Work
Technical:
Reliable internet connection (5+ Mbps recommended)
Computer/laptop
Quiet workspace (if on calls)
Professional:
Minimum 1-2 years coding experience (most companies require this)
CPC certification (highly preferred, often required)
98%+ accuracy record
Legal:
Indian PAN and bank account (for payments)
Compliance with Indian tax laws (freelance income needs reporting)
Language:
Fluent English (written and verbal)
Understanding of American healthcare terminology
How to Land Remote International Coding Job
Step 1: Build Experience Locally (1-2 Years)
Work in India first. This builds your coding skills and accuracy. US employers want experienced coders, not freshers.
Step 2: Get CPC Certified
Get your CPC certification from AAPC. This is standard requirement for quality remote positions.
Step 3: Build Portfolio
Document your work: accuracy rates, types of records coded, complexity handled, audit results if you’ve been reviewed.
Step 4: Connect with Recruiters
- LinkedIn: Search “medical coding recruiter” + “India” or “remote”
- Platforms: Upwork, Freelancer, Toptal (for freelance work)
- Direct: Research US healthcare BPOs, check their careers pages
- Professional: Join AAPC, access their job board
Step 5: Application & Interview
- Apply to remote positions
- Technical interview: They’ll ask you to code sample records
- Accuracy test: You’ll be evaluated on correctness
- Professionalism: They’ll assess communication
Step 6: Onboarding
Once hired, you’ll get training on their specific systems, compliance requirements, and processes.
Reality Check: Remote Work Challenges
Not as Easy as It Sounds:
- US medical records are different from Indian records
- American healthcare terminology is specific
- Accuracy standards are very strict
- Can be competitive (lots of coders want these jobs)
Time Zone Challenges:
- Might need to work odd hours
- Meetings could be early morning or late evening IST
Payment Issues:
- International payment sometimes requires SWIFT/wire transfers
- Startup costs (good internet, dedicated workspace)
- Inconsistent flow if working as freelancer
But Worth It:
Despite challenges, remote international coding remains one of the best ways for Indian medical coders to earn significantly. Many coders’ first remote job leads to better opportunities as their experience and reputation grow.
Landing Your First Medical Coding Job: Complete Strategy
Now let’s get you actually hired.
Resume for Medical Coders
Your medical coding resume needs to immediately convince the hiring manager: “This person will code accurately and quickly.”
Resume Template:
text
[YOUR NAME]
City, State | Phone: +91-XXXXX-XXXXX | Email: yourname@email.com | LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/yourprofile
PROFESSIONAL SUMMARY
Accurate and detail-oriented Medical Coding professional with [X months/years] of coding experience. Proficient in ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems with [98%+] accuracy rate. CPC certified [or certification in progress]. Committed to optimizing healthcare revenue through accurate medical coding and compliance.
CERTIFICATIONS
- CPC (Certified Professional Coder) – AAPC | License #: XXXXX | Valid until: [Date]
- Medical Coding Certificate – [Institute Name] | [Year]
- [Any other relevant certifications]
TECHNICAL SKILLS
Medical Coding: ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS, CPT, HCPCS coding systems
Specializations: [If you have specialty experience, e.g., “Orthopedic coding, Cardiac coding”]
Software: [Epic, Cerner, Medicode, etc. – whichever you’ve used]
Accuracy: 98%+ consistent accuracy across all coding assignments
Productivity: Codes 60-80+ charts daily maintaining quality standards
PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE
Medical Coding Trainee | [Hospital/Organization Name] | [City] | [Dates]
- Coded 40-60 patient medical records daily using ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems
- Maintained 97-98% accuracy rate with <0.5% denial rate
- Coded across multiple departments (General Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics)
- Researched and applied complex coding guidelines to accurately classify diagnoses and procedures
- Received feedback from supervisors on accuracy and professionalism (positive evaluations)
- [If internship had specific achievements]: Coded 500+ records with zero compliance violations
[If you have additional experience]:
Medical Coding Intern | [Healthcare Organization] | [City] | [Dates]
- [Details of responsibilities and achievements with metrics]
EDUCATION
Medical Coding Certificate | [Institute Name] | [Year]
- Completed comprehensive training in ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS coding systems
- [If you did well]: Final exam score: 85%+ or completed with distinction
- [If training focused on specifics]: Specialized training in medical terminology and healthcare billing
[Your Educational Background]:
[12th Grade / Bachelor’s Degree] | [School/College Name] | [Year]
LANGUAGES
English: Fluent (written and verbal)
Hindi: [Proficiency level]
[Any other languages]
KEYWORDS TO INCLUDE (for ATS scanning)
- ICD-10 Coding • CPT Coding • HCPCS • Medical Coding • Healthcare Billing
- Medical Records • Coding Accuracy • Healthcare Compliance • CPC Certified
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) • [Your specialty if any]
Key Points About Medical Coding Resumes:
- Lead with Accuracy: First thing coding employers look for is accuracy. Put this prominently.
- Quantify Everything: Instead of “Good at medical coding,” write “Maintains 98%+ accuracy rate, codes 70+ charts daily”
- Certifications Front & Center: If CPC certified, put it right after your name. CPC is your biggest value-add.
- Technical Skills Section: Make it easy for employers to see exactly which coding systems and software you know.
- Experience Over Education: If you have coding experience/internship, emphasize that. Healthcare institutions care more about your coding ability than your general educational background.
- Avoid Vague Claims: Don’t write “skilled at medical coding.” Write “Proficient in ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS, CPT, and HCPCS with 98.5% accuracy record”
Where to Find Medical Coding Jobs
Online Job Portals:
- Naukri.com – Search “Medical Coder” + “Your City”
- Indeed.com – Good for hospital and BPO positions
- LinkedIn Jobs – Better for BPO and corporate positions
- Internshala – For internship to employment pathway
- Glassdoor – Check company reviews while applying
BPO/Outsourcing Companies (Actively Hire Coders):
- Accenture
- Cognizant
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Genpact
- Infosys
- IBM
Direct Hospital Applications:
- Research 20-30 hospitals in your city
- Visit their websites, find HR contact
- Email your resume directly to HR
Specialized Medical Coding Job Portals:
- AAPC Job Board (for certified professionals)
- Medical Coding specific recruitment agencies
- Healthcare staffing companies
Remote/International Positions:
- Upwork (search “medical coder”)
- Freelancer.com
- Toptal
- RemoteOK (filter healthcare)
- FlexJobs (vetted remote jobs)
Interview Preparation for Medical Coders
Medical coding interviews typically include:
- Coding Test (Most Important)
You’ll be given 5-10 medical records and asked to code them. Time limit usually 30-60 minutes.
Test Strategy:
- Read the ENTIRE record before coding (don’t skim)
- Code all diagnoses mentioned in the record
- Don’t miss secondary diagnoses
- Double-check your codes (use code references)
- Explain your coding choices if asked
- Accuracy matters more than speed initially
- Behavioral Questions
Q: “Tell me about a coding error you made. How did you handle it?”
Good Answer: “During my training, I initially coded a diagnosis as principal diagnosis when it was actually a secondary diagnosis. My supervisor caught it during review. I immediately researched the coding guidelines to understand the difference. Now I always verify principal vs. secondary diagnoses before finalizing my coding. This experience taught me the importance of accuracy and thoroughness.”
Q: “How do you stay updated with coding changes?”
Good Answer: “Medical coding guidelines change yearly. I stay current by reading AAPC updates, attending webinars on coding changes, subscribing to coding newsletters, and reviewing new guidelines with colleagues. I understand that outdated coding leads to claim denials, so continuous learning is essential.”
Q: “How do you handle pressure to code quickly?”
Good Answer: “I understand that coding productivity matters, but accuracy is non-negotiable. My approach is to build speed through experience and system familiarity, not by cutting corners. If I’m approaching my deadline and still have complex records, I’d communicate to my supervisor rather than compromise accuracy. I’d rather code 60 charts at 98% accuracy than 80 charts at 95% accuracy.”
- Technical Knowledge Questions
They’ll ask random coding questions to test knowledge:
Q: “When is a diagnosis considered a ‘principal diagnosis’?”
Good Answer: “Principal diagnosis is the condition that caused the patient’s hospital admission or the condition being treated during the visit. For example, if a patient comes to the hospital with chest pain and is diagnosed with myocardial infarction, the MI is the principal diagnosis. Any other conditions found during the visit (like diabetes) would be secondary diagnoses. Getting this right is crucial because insurers pay based on the principal diagnosis.”
- Behavioral Assessment
They’re assessing:
- Your attention to detail (do you listen carefully?)
- Your communication (can you explain your thinking?)
- Your problem-solving (how do you handle uncertainty?)
- Your attitude (are you coachable? Do you care about accuracy?)
Salary Negotiation for Medical Coders
When you receive an offer:
Research First:
- Check Glassdoor salary data for that company
- Ask peers what entry-level coders earn
- Know the typical range (usually ₹2-3 LPA for CPC-certified freshers)
Negotiation Script:
“Thank you for the offer. I’m excited about joining [Company]. Based on my CPC certification, [X] months of coding experience, and the market rates for medical coders in [City], I was expecting ₹[X amount]. Would there be flexibility?”
What’s Usually Negotiable:
- Base salary (10-15% room usually)
- Performance bonus structure
- Professional development support (CPC exam reimbursement)
- Leave entitlements
If They Can’t Increase:
“I understand the budget constraints. Would we revisit salary after my 6-month performance review? Additionally, would the company support any further certifications I pursue?”
Medical Coding Career Pitfalls: Avoid These Mistakes
Mistake 1: Skipping Certification Because “I Can Get a Job Without It”
True, you can get an entry-level job without CPC. But advancement without it is nearly impossible. You’ll hit a salary ceiling at ₹3-3.5 LPA and struggle to move forward.medesunglobal
Instead: Get CPC certified within your first year of work. Yes, it requires study. Yes, the exam is challenging. But it’s a worthwhile investment. The salary increase alone recovers your investment in 3-4 months.
Mistake 2: Prioritizing Speed Over Accuracy
New coders sometimes think “I’ll code faster” = “I’ll earn more.” Wrong. Wrong. Wrong.blogs.docthub
Accurate coding at moderate speed (70 charts/day at 98% accuracy) = Reliable, valued coder
Fast inaccurate coding (100 charts/day at 94% accuracy) = Problem coder to be avoided
Hospital lose money on wrong codes. They WILL eventually fire fast but inaccurate coders. Accuracy first, speed develops naturally.blogs.docthub
Instead: Always prioritize accuracy. Speed comes naturally with experience. Build your reputation as “that coder who catches details others miss.”
Mistake 3: Not Specializing
General coders earn ₹3-5 LPA. Specialized coders (orthopedic, cardiac, oncology, etc.) earn ₹4.5-7 LPA+.blogs.docthub
Instead: After 1-2 years of general coding, choose a specialization. Learn that specialty deeply. Become THE person your hospital calls for complex cases in that specialty.
Mistake 4: Ignoring Compliance & Regulations
Medical coding isn’t just technical. It’s legally regulated. Wrong coding can be classified as fraud (intentional or not).swaasa+1
Instead: Understand HIPAA compliance, medical coding ethics, billing fraud consequences. Attend compliance training. Never knowingly code incorrectly just to help a friend or please a doctor.
Mistake 5: Staying in First Job Too Long Without Growth
If you’re in the same role at the same salary after 3+ years, you’re not progressing.blogs.docthub
Instead: Every 2-3 years, make a strategic move:
- Year 1-2: Build skills in entry role
- Year 2-3: Transition to specialized coding or audit role (salary jump)
- Year 4-5: Move to senior/lead role or switch to BPO/remote work (salary jump)
- Year 5-7: Move to management or specialist track (bigger salary jump)
Your 90-Day Action Plan: From Zero to Employed Medical Coder
Month 1: Foundation & Learning (Days 1-30)
Week 1:
- ☐ Research medical coding training institutes in your city
- ☐ Enroll in medical coding course (certificate or diploma)
- ☐ Set up dedicated study space
- ☐ Create LinkedIn profile (mark “Open to Medical Coding Opportunities”)
Week 2:
- ☐ Start medical coding course/training
- ☐ Begin medical terminology learning
- ☐ Join online medical coding communities (Facebook groups, subreddits)
- ☐ Watch YouTube videos on ICD-10, CPT basics
Week 3:
- ☐ Continue course lessons
- ☐ Start practicing with sample medical records
- ☐ Research CPC certification details
- ☐ Connect with people working in medical coding on LinkedIn
Week 4:
- ☐ Complete initial course modules
- ☐ Practice coding 20-30 sample charts
- ☐ Review your accuracy (aiming for 90%+ during learning)
- ☐ Make list of 15-20 target hospitals/companies
End of Month 1: Foundational knowledge in place, initial practice completed, job search prep begun
Month 2: Practical Skills & Job Applications (Days 31-60)
Week 5:
- ☐ Continue intensive course (if multi-month program)
- ☐ Practice coding 50+ sample charts daily
- ☐ Aim for 95%+ accuracy on practice charts
- ☐ Start applying to entry-level positions
Week 6:
- ☐ Apply to 10-15 medical coding positions
- ☐ Customize resume for each application (use template provided)
- ☐ Prepare answers to interview questions
- ☐ Update LinkedIn profile with medical coding skills
Week 7:
- ☐ Complete your course if multi-month program
- ☐ Apply to 10+ more positions
- ☐ Follow up on previous applications (if no response)
- ☐ Start direct hospital outreach (email HR managers)
Week 8:
- ☐ Interviews likely starting—prepare thoroughly
- ☐ Apply to 5-10 more positions
- ☐ Practice coding speed (aim for 40-50 charts/day while maintaining 98% accuracy)
- ☐ Research salary ranges for your city/experience level
End of Month 2: 30-40+ applications submitted, 3-5 interviews completed, interviews practice comprehensive
Month 3: Securing Position & Starting (Days 61-90)
Week 9:
- ☐ Continue interviews
- ☐ Prepare offer negotiation strategies
- ☐ Begin CPC exam preparation (even if not required for first job, start planning)
- ☐ Practice coding 70-80 charts/day at 98% accuracy
Week 10:
- ☐ Receive job offer (likely by now)
- ☐ Negotiate salary if applicable
- ☐ Prepare documentation (address proof, PAN, bank account, etc.)
- ☐ Celebrate! You got your first medical coding job!
Week 11:
- ☐ Start your job
- ☐ Complete orientation
- ☐ Learn company’s coding systems and processes
- ☐ Ask lots of questions
- ☐ Build relationships with colleagues
Week 12:
- ☐ Focus on accuracy (speed will develop)
- ☐ Understand common diagnoses you’re coding
- ☐ Get feedback from supervisors
- ☐ Plan CPC certification study (if not already certified)
End of Month 3: First medical coding job secured, you’re earning, learning, and building your career!
Closing: Your Medical Coding Journey Begins
You’ve reached the end of this guide. But unlike many career guides that leave you feeling overwhelmed or uncertain, you now have a concrete roadmap.
Here’s what’s possible with medical coding:
- Quick entry: 3-6 months to employment vs. 5+ years for medicine
- Decent starting income: ₹2-3 LPA while you’re just beginning
- Clear growth: ₹25+ LPA within 10 years for strategic career moves
- Remote work: Earn ₹25-40 LPA from your home coding for international clients
- No patient contact: If you prefer not to interact with patients, medical coding offers that
- Accuracy mastery: Build a career on precision, attention to detail, and expertise
- Job security: Healthcare will always need coders; this job won’t disappear
Medical coding isn’t glamorous. It’s not like being a doctor. You won’t be on the front lines of patient care. But it’s stable, rewarding, growing, and genuinely valuable to the healthcare system.
You translate medical information into the universal language that keeps healthcare operational. That matters.
Now, take action. Research institutes. Enroll in a course. Start learning. Apply for that first job. Build this career.
Your medical coding journey doesn’t start someday. It starts today.
Good luck, future medical coder. The healthcare industry needs your accuracy and attention to detail.
