Debugging is an essential skill for Java developers. Using Ide Debuggers such as IntelliJ or Eclipse helps to track issues efficiently. Analyzing the stack mark and adding meaningful logs may indicate errors. Units prevent testing regression, while avoiding disabled check errors. Profiling tools help to detect performance issues. Mastery of these debugging tips for Java improves the quality and efficiency of the code. Practicing with a breakpoints and runtime analysis helps reduce the bug. Adopting these debugging tips for Java ensures smooth project delivery and cleaner, more reliable code.
Why Debugging is Important
Before diving into specific debugging techniques, it is important to understand why debugging software plays an important role in development:
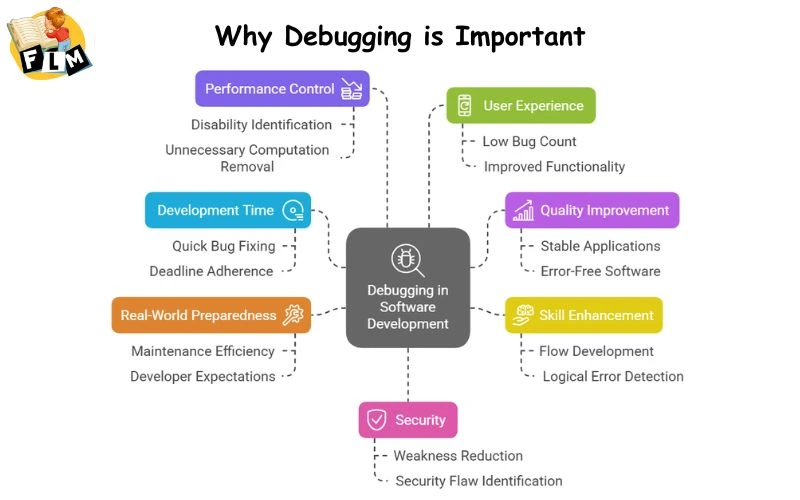
- Reduces the Time of Development: I quickly identify and fix the bugs to prevent the delay in the project deadline.
- Improvement in Quality: Proper debugging ensures stable and error-free applications.
- Problem-Solution Enhances Skills: Debugging developers help develop the flow and detect logical errors.
- Prepare for Real-World Challenges: companies hope that developers are expected to be efficiently debugged during software development and maintenance.
- Controls the Performance: debugging helps in finding disabilities, slow performance issues and unnecessary computations.
- User Improves Experience: Low bugs means smooth app performance and better purpose.
- Security Reduces Weaknesses: proper debugging helps identify potential security flaws.
Common Debugging Techniques
Making use of Print Statements
- Explanation:
- One of the simplest debugging techniques is using a print statement to examine the variable values and track the flow of execution.
- When to use:
- Check the variable values at different stages of execution.
- If a function or method is being executed correctly, then identify.
- Debugging loops and conditions.
- Limit:
- Excessive print statements can disorganize the output and reduce readability.
Utilizing a Debugger Tool
- Explanation:
- A Debugger tool allows developers to set breakpoints, inspect the values, and control the program execution.
- When to Use:
- Debugging applications in the environment where the print statement is disabled.
- Analysis of stack marks and understanding flow.
Using an Integrated Debugger
- Explanation:
- Most growth environments provide underlying debugging tools with features such as breakpoints, variable inspection and phase execution.
- How to Use:
- Set the Breakpoint in the code.
- Run the program in debug mode.
- Steps through code to analyze values and execution flows.
- Benefits:
- Provides real-time insight into execution.
- A conditional breakpoint allows for efficient debugging.
Analyzing Stack Traces
- Explanation:
- Stack marks help to identify an exception leading to an exception showing an error showing the call hierarchy.
- When to Use:
- Runtime exceptions such as missing values, out-of-bounds errors and invalid arguments.
- Debugging Tip:
- Read the stack trace from top to bottom to understand the error source.
Using Loggers
- Explanation:
- Unlike print statements, loggers allow structured and configurable logging, making the production easier debugging in the environment.
- Best Practices:
- For better classification, use various logging levels (information, debug, warning, error).
- Avoid logging on to sensitive information in production logs.
- To maintain debugging history, log into external files.
Checking Null and Exception Handling
- Explanation:
- Null values and unhandled exceptions are common causes of runtime failures.
- Debugging Tip:
- Always check the zero values before using the object or variable.
- Use an error-handling mechanism to prevent unexpected crashes.
- Apply appropriate exception handling techniques to prevent silent failures.
Memory and Performance Analysis
- Explanation:
- Memory leaks and inefficient code apps can degrade application performance.
- Tools to use:
- Memory Analyzer: Memory helps in detecting leaks.
- Performance Monitoring Equipment: Tracks performance in real time.
- Profiling Tool: Identify excessive resource consumption.
Unit Testing for Debugging
- Explanation:
- Writing a unit test helps in identifying bugs quickly in development.
- Best practices:
- Write testing cases for important methods and edge cases.
- Use claims to validate the expected behavior.
- Test frequently to quickly detect issues.
- Apply automatic tests for continuous debugging and quality assurance.
Using Breakpoints and Watch Variables
- Explanation:
- Breakpoint developers allow developers to prevent execution at specific points and inspect values.
- Debugging Tip:
- Use conditional breakpoints only to prevent execution when a specific situation is met.
- See variables to track changes in values during execution.
- Use step-by-step debugging for intensive analysis.
Refactoring and Code Review for Debugging
- Explanation:
- The complex code is difficult to debug. Refactoring and peer reviews helps identify possible issues.
- Best Practices:
-
- Follow clean code principles for stability.
- Regularly review the code with team members to detect hidden bugs.
- Use code lines and static analysis tools for initial bug detection.
- Remote Debugging
- Remote is used to debug the application on the server.
- Enable remote debugging by configuring the environment correctly.
- Connect to the remote process using a debugging tool.
- Using Performance Monitoring Tools
- The runtime for performance analysis helps capture the information.
- The production environment is useful for identifying CPU, memory and threading issues.
- Slow response allows time and bottleneck detection.
- Thread debugging:
- Use thread dump to analyze the deadlock and performance of performance.
- Use synchronized operations and proper consistency management to avoid race conditions.
- Identify multi-threading issues through consent analysis.
- Debugging Database issues
- Enable SQL logging to track queries and track execution time.
- Use a database profiling tool to identify slow questions.
- Ensure proper connection handling to avoid memory leaks.
- Adapt to sequencing and query structures for rapid execution.
- Using Static Code Analysis Tools
- Automatic code analysis improves quality and stability.
- Helps in growing disabilities and potential bugs in development.
- Security identifies weaknesses before deployment.
- Continuous Integration and Debugging
- Apply continuous integration tools for automatic debugging.
- Use automatic reports to track without trends and fix recurring issues.
- Enable real-time notifications for new debugging alerts.
Conclusion
To write stable and efficient applications, it is necessary to expect Debugging Tips for Java. Using debugging tools, analyzing stack trace, taking advantage of loggers, and applying proper error, developers can reduce debugging time and improve quality.
Additionally, unit testing, remote debugging and performing performance analysis equipment helps maintain strong applications. Debugging is not only about fixing errors – it is about understanding how the execution flows, predicts potential failures, and adapters the performance.
By continuously applying these Debugging Tips for Java, developers can be more efficient to identify and solve issues, leading to better software development practices and career growth.
In addition, the latest debugging tools, automation framework and maintaining best practices ensure continuous improvement in software quality. As the debugging develops with new techniques, updates with modern debugging techniques will give developers a competitive lead in the industry.
Start applying these debugging techniques today to enhance the skills of solving your problem and create more efficient, reliable applications!
Suggested Articles:
-
What’s Next After Completing Your Java Full Stack Course
-
Top Coding Challenges for Java Developers
-
Effective Learning Strategies for Java
Future-Proof Your Career with FLM’s AI-Powered Java Full Stack Development!
Java Full Stack Developer Training
Learn Java, Spring Boot, React.js, SQL, and AI automation to build powerful web applications. AI is transforming software development, and companies need skilled Java full stack developers who can integrate AI-driven solutions. This 5+ month live, interactive training will help you master real-world projects, automation tools, and industry best practices.
What You’ll Gain?
- High Demand – AI Skills Give You a Competitive Edge
- Earn ₹12 LPA+ with Java Full Stack & AI Expertise
- 100% Live, Expert-Led Training
- AI-Powered Development – Automate Coding & Debugging
- 7 Major & 7 Mini Real-World Projects for Hands-On Experience
- Mock Interviews, Resume Building & Career Guidance
- Exclusive: 2-Year Recording Access for the First 100 Enrollees
- Job-Ready Curriculum with Real-World Applications
Unlock your future with FLM’s AI-Powered Java Full Stack Development
Limited Seats Available – Enroll Now!
Visit: frontlinesedutech.com | Click Here to Enroll
WhatsApp: 8333077727


